Ribosomes from an oxazolidinone-resistant mutant confer resistance to eperezolid in a Staphylococcus aureus cell-free transcription-translation assay
- PMID: 9559817
- PMCID: PMC105576
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.4.947
Ribosomes from an oxazolidinone-resistant mutant confer resistance to eperezolid in a Staphylococcus aureus cell-free transcription-translation assay
Abstract
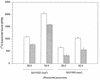
Oxazolidinone-resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus, isolated with a spiral plating technique, had a 16-fold higher MIC (2 versus 32 microg/ml) of eperezolid when compared to the parental sensitive strain. Eperezolid inhibited in vitro protein translation with 50% inhibitory concentrations of 30 microM for the oxazolidinone-sensitive S30 extract and 75 microM for the resistant extract. Experiments mixing various combinations of S100 and crude ribosome preparations from oxazolidinone-sensitive and -resistant S. aureus strains in a transcription-translation assay demonstrated that the resistant determinant resided within the ribosomal fraction. Ribosomes from the oxazolidinone-resistant strain bound less drug than ribosomes from the sensitive strain, indicating that the ribosome is the site of action for the oxazolidinones. These experiments demonstrate that an alteration of the ribosome is responsible for some or all of the oxazolidinone resistance observed in the S. aureus mutant.
Figures


References
-
- Barbachyn M R, Hutchinson D K, Brickner S J, Cynamon M H, Kilburn O J, Klemens S P, Glickman S E, Grega K C, Hendges S K, Toops D S, Ford C W, Zurenko G E. Identification of a novel oxazolidinone (U-100480) with potent antimycobacterial activity. J Med Chem. 1996;39:680–685. - PubMed
-
- Brickner S J, Hutchinson D K, Barbachyn M R, Manninen P R, Ulanowicz D A, Garmon S A, Grega K C, Hendges S K, Toops D S, Ford C W, Zurenko G E. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of U-100592 and U-100766, two oxazolidinone antibacterial agents for the potential treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacterial infections. J Med Chem. 1996;39:673–679. - PubMed
-
- Brumfitt W, Hamilton-Miller J M T. Antibacterial oxazolidinones: in vitro activity of a new analogue, E3709. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;15:621–625. - PubMed
-
- Daly J S, Eliopoulos G M, Reiszner E, Moellering R C. Activity and mechanism of action of DuP 105 and DuP 721, new oxazolidinone compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988;21:721–730. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

