Alginate lyase promotes diffusion of aminoglycosides through the extracellular polysaccharide of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 9559826
- PMCID: PMC105585
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.4.974
Alginate lyase promotes diffusion of aminoglycosides through the extracellular polysaccharide of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
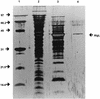
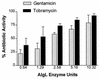
We demonstrated that a 2% suspension of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate completely blocked the diffusion of gentamicin and tobramycin, but not that of carbenicillin, illustrating how alginate production can help protect P. aeruginosa growing within alginate microcolonies in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) from the effects of aminoglycosides. This aminoglycoside diffusion barrier was degraded with a semipurified preparation of P. aeruginosa alginate lyase, suggesting that this enzyme deserves consideration as an adjunctive agent for CF patients colonized by mucoid strains of P. aeruginosa.
Figures


References
-
- Allison D G, Matthews M J. Effect of polysaccharide interactions on antibiotic susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992;73:484–488. - PubMed
-
- Boyd A, Ghosh M, May T B, Shinabarger D, Keogh R, Chakrabarty A M. Sequence of the algL gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and purification of its alginate lyase product. Gene. 1993;131:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Caswell R C, Gacesa P, Lutrell K E, Weightman A J. Molecular cloning and heterologous expression of a Klebsiella pneumoniae gene encoding alginate lyase. Gene. 1989;75:127–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

