Phospholipid composition of the mammalian red cell membrane can be rationalized by a superlattice model
- PMID: 9560211
- PMCID: PMC20196
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.9.4964
Phospholipid composition of the mammalian red cell membrane can be rationalized by a superlattice model
Abstract
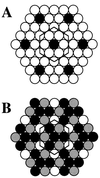
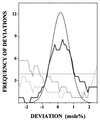
Although the phospholipid composition of the erythrocyte membrane has been studied extensively, it remains an enigma as to how the observed composition arises and is maintained. We show here that the phospholipid composition of the human erythrocyte membrane as a whole, as well as the composition of its individual leaflets, is closely predicted by a model proposing that phospholipid head groups tend to adopt regular, superlattice-like lateral distributions. The phospholipid composition of the erythrocyte membrane from most other mammalian species, as well as of the platelet plasma membrane, also agrees closely with the predictions of the superlattice model. Statistical analyses indicate that the agreement between the observed and predicted compositions is highly significant, thus suggesting that head group superlattices may indeed play a central role in the maintenance of the phospholipid composition of the erythrocyte membrane.
Figures

References
-
- Somerharju P, Virtanen J A, Eklund K, Vainio P, Kinnunen P. Biochemistry. 1985;24:2773–2781. - PubMed
-
- Virtanen J A, Somerharju P, Kinnunen P K J. J Mol Electron. 1987;4:233–236.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

