Modification of bacterial artificial chromosomes through chi-stimulated homologous recombination and its application in zebrafish transgenesis
- PMID: 9560239
- PMCID: PMC20224
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.9.5121
Modification of bacterial artificial chromosomes through chi-stimulated homologous recombination and its application in zebrafish transgenesis
Abstract
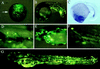
The modification of yeast artificial chromosomes through homologous recombination has become a useful genetic tool for studying gene function and enhancer/promoter activity. However, it is difficult to purify intact yeast artificial chromosome DNA at a concentration sufficient for many applications. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are vectors that can accommodate large DNA fragments and can easily be purified as plasmid DNA. We report herein a simple procedure for modifying BACs through homologous recombination using a targeting construct containing properly situated Chi sites. To demonstrate a usage for this technique, we modified BAC clones containing the zebrafish GATA-2 genomic locus by replacing the first coding exon with the green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene. Molecular analyses confirmed that the modification occurred without additional deletions or rearrangements of the BACs. Microinjection demonstrated that GATA-2 expression patterns can be recapitulated in living zebrafish embryos by using these GFP-modified GATA-2 BACs. Embryos microinjected with the modified BAC clones were less mosaic and had improved GFP expression in hematopoietic progenitor cells compared with smaller plasmid constructs. The precise modification of BACs through Chi-stimulated homologous recombination should be useful for studying gene function and regulation in cultured cells or organisms where gene transfer is applicable.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

