Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts
- PMID: 9564564
- PMCID: PMC106833
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.11.2.267
Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts
Abstract
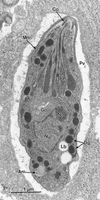
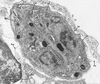
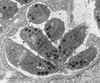
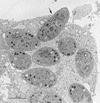
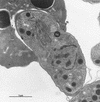
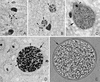
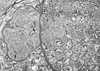
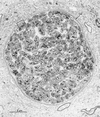
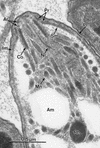
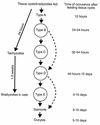
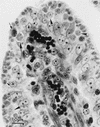
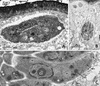
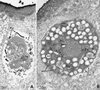
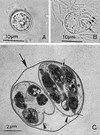
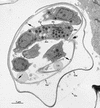
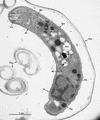
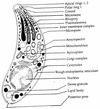
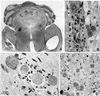
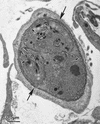
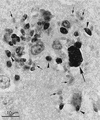
Infections by the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii are widely prevalent world-wide in animals and humans. This paper reviews the life cycle; the structure of tachyzoites, bradyzoites, oocysts, sporocysts, sporozoites and enteroepithelial stages of T. gondii; and the mode of penetration of T. gondii. The review provides a detailed account of the biology of tissue cysts and bradyzoites including in vivo and in vitro development, methods of separation from host tissue, tissue cyst rupture, and relapse. The mechanism of in vivo and in vitro stage conversion from sporozoites to tachyzoites to bradyzoites and from bradyzoites to tachyzoites to bradyzoites is also discussed.
Figures




References
-
- Appleford P J, Smith J E. Toxoplasma gondii: the growth characteristics of three virulent strains. Acta Trop. 1997;65:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Bertoli F, Espino M, Arosemena J R, Fishback J L, Frenkel J K. A spectrum in the pathology of toxoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1995;119:214–224. - PubMed
-
- Beverley J K A. A rational approach to the treatment of toxoplasmic uveitis. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1958;78:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Bjerkås I. Neuropathology and host-parasite relationship of acute experimental toxoplasmosis of the blue fox (Alopex lagopus) Vet Pathol. 1990;27:381–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

