Production of mice deficient in genes for interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-1alpha/beta, and IL-1 receptor antagonist shows that IL-1beta is crucial in turpentine-induced fever development and glucocorticoid secretion
- PMID: 9565638
- PMCID: PMC2212263
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.9.1463
Production of mice deficient in genes for interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-1alpha/beta, and IL-1 receptor antagonist shows that IL-1beta is crucial in turpentine-induced fever development and glucocorticoid secretion
Abstract
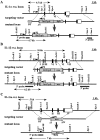
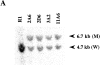
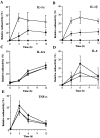
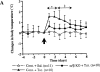
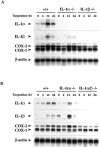
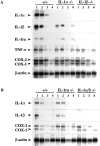
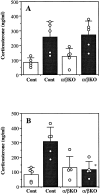
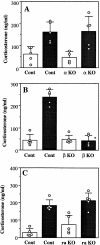
Interleukin (IL)-1 is a major mediator of inflammation and exerts pleiotropic effects on the neuro-immuno-endocrine system. To elucidate pathophysiological roles of IL-1, we have first produced IL-1alpha/beta doubly deficient (KO) mice together with mice deficient in either the IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, or IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) genes. These mice were born healthy, and their growth was normal except for IL-1ra KO mice, which showed growth retardation after weaning. Fever development upon injection with turpentine was suppressed in IL-1beta as well as IL-1alpha/beta KO mice, but not in IL-1alpha KO mice, whereas IL-1ra KO mice showed an elevated response. At this time, expression of IL-1beta mRNA in the diencephalon decreased 1.5-fold in IL-1alpha KO mice, whereas expression of IL-1alpha mRNA decreased >30-fold in IL-1beta KO mice, suggesting mutual induction between IL-1alpha and IL-1beta. This mutual induction was also suggested in peritoneal macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide in vitro. In IL-1beta KO mice treated with turpentine, the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (EC 1.14.99.1) in the diencephalon was suppressed, whereas it was enhanced in IL-1ra KO mice. We also found that glucocorticoid induction 8 h after turpentine treatment was suppressed in IL-1beta but not IL-1alpha KO mice. These observations suggest that IL-1beta but not IL-1alpha is crucial in febrile and neuro-immuno-endocrine responses, and that this is because IL-1alpha expression in the brain is dependent on IL-1beta. The importance of IL-1ra both in normal physiology and under stress is also suggested.
Figures


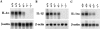


Similar articles
-
IL-6 and IL-1 beta in fever. Studies using cytokine-deficient (knockout) mice.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Sep 29;856:33-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb08310.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9917862
-
Role of endogenous interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in regulating fever induced by localised inflammation in the rat.J Physiol. 2001 Feb 15;531(Pt 1):171-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0171j.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11179401 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperresponsive febrile reactions to interleukin (IL) 1alpha and IL-1beta, and altered brain cytokine mRNA and serum cytokine levels, in IL-1beta-deficient mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 18;94(6):2681-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2681. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9122256 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory response in interleukin-1 beta-deficient mice: comparison with other cytokine-related knock-out mice.J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Apr;59(4):489-93. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.4.489. J Leukoc Biol. 1996. PMID: 8613694 Review.
-
The interleukin-1 system: receptors, ligands, and ICE in the brain and their involvement in the fever response.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 May 1;840:51-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09548.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9629236 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice develop autoimmune arthritis due to intrinsic activation of IL-17-producing CCR2(+)Vγ6(+)γδ T cells.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 25;6:7464. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8464. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26108163 Free PMC article.
-
Serial Systemic Injections of Endotoxin (LPS) Elicit Neuroprotective Spinal Cord Microglia through IL-1-Dependent Cross Talk with Endothelial Cells.J Neurosci. 2020 Nov 18;40(47):9103-9120. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0131-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33051350 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1α induces thrombopoiesis through megakaryocyte rupture in response to acute platelet needs.J Cell Biol. 2015 May 11;209(3):453-66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201410052. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25963822 Free PMC article.
-
alpha2-macroglobulin- and murinoglobulin-1- deficient mice. A mouse model for acute pancreatitis.Am J Pathol. 1999 Sep;155(3):983-93. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65198-x. Am J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10487856 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive mechanisms during viral infectious diseases.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;677:431-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-869-0_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20941625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–2147. - PubMed
-
- Durum, S.K., and J.J. Oppenheim. 1993. Proinflammatory cytokines and immunity. In Fundamental Immunology, 3rd ed. W.E. Paul, editor. Raven Press, Ltd., New York. 801– 835.
-
- Tocci, M.J., and J.A. Schmidt. 1997. Interleukin-1: structure and function. In Cytokines in Health and Disease, 2nd ed. D.G. Remick and J.S. Friedland, editors. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York. 1–27.
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991;77:1627–1652. - PubMed
-
- Silver ARJ, Masson WK, George AM, Adam J, Cox R. The IL-1α and β genes are closely linked (<70 kb) on mouse chromosome 2. Somatic Cell Mol Genet. 1990;16:549–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

