Tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation: enhancement of C/EBPbeta-induced activation by c-Jun
- PMID: 9566900
- PMCID: PMC110660
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2815
Tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation: enhancement of C/EBPbeta-induced activation by c-Jun
Abstract
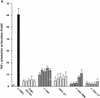
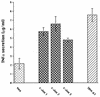
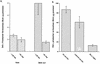
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) is a key regulatory cytokine whose expression is controlled by a complex set of stimuli in a variety of cell types. Previously, we found that the monocyte/macrophage-enriched nuclear transcription factor C/EBPbeta played an important role in the regulation of the TNF alpha gene in myelomonocytic cells. Abundant evidence suggests that other transcription factors participate as well. Here we have analyzed interactions between C/EBPbeta and c-Jun, a component of the ubiquitously expressed AP-1 complex. In phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-treated Jurkat T cells, which did not possess endogenous C/EBPbeta, expression of c-Jun by itself had relatively little effect on TNF alpha promoter activity. However, the combination of C/EBPbeta and c-Jun was synergistic, resulting in greater than 130-fold activation. This effect required both the leucine zipper and DNA binding domains, but not the transactivation domain, of c-Jun, plus the AP-1 binding site centered 102/103 bp upstream of the transcription start site in the TNF alpha promoter. To determine if C/EBPbeta and c-Jun might cooperate to regulate the cellular TNF alpha gene in myelomonocytic cells, U937 cells that possess endogenous C/EBPbeta and were stably transfected with either wild-type c-Jun or the transactivation domain deletion mutant (TAM-67) were examined. U937 cells expressing ectopic wild-type c-Jun or TAM-67 secreted over threefold more TNF alpha than the control line in response to PMA plus lipopolysaccharide. Transient transfection of the U937 cells expressing TAM-67 suggested that TAM-67 binding to the -106/-99-bp AP-1 binding site cooperated with endogenous C/EBPbeta in the activation of the -120 TNF alpha promoter-reporter. DNA binding assays using oligonucleotides derived from the TNF alpha promoter suggested that C/EBPbeta and c-Jun interact in vitro and that the interaction may be DNA dependent. Our data demonstrate that the TNF alpha gene is regulated by the interaction of the ubiquitous AP-1 complex protein c-Jun and the monocyte/macrophage-enriched transcription factor C/EBPbeta and that this interaction contributes to the expression of the cellular TNF alpha gene in myelomonocytic cells. This interaction was unique in that it did not require the c-Jun transactivation domain, providing new insight into the cell-type-specific regulation of the TNF alpha gene.
Figures



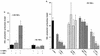
Similar articles
-
Regulation of TNF-alpha expression in normal macrophages: the role of C/EBPbeta.Cytokine. 2000 Aug;12(8):1171-81. doi: 10.1006/cyto.2000.0691. Cytokine. 2000. PMID: 10930293
-
Transcriptional induction of collagenase-1 in differentiated monocyte-like (U937) cells is regulated by AP-1 and an upstream C/EBP-beta site.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):11840-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.11840. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9115242
-
TNF-alpha gene expression in macrophages: regulation by NF-kappa B is independent of c-Jun or C/EBP beta.J Immunol. 2000 Apr 15;164(8):4277-85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.8.4277. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10754326
-
Transcriptional activation of scavenger receptor expression in human smooth muscle cells requires AP-1/c-Jun and C/EBPbeta: both AP-1 binding and JNK activation are induced by phorbol esters and oxidative stress.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Sep;18(9):1440-9. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.9.1440. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9743233
-
Interferon-gamma suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 promoter activity by inhibiting C-Jun and C/EBPbeta binding.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Aug;27(8):1752-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.144352. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17556653
Cited by
-
A novel polyamine analog inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2769-77. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12855657 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid Treatment in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Overview on Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Benefit.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12138. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512138. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CHOP enhancement of gene transcription by interactions with Jun/Fos AP-1 complex proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7589-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7589. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523647 Free PMC article.
-
Early activation of hepatic NFkappaB and NF-IL6 in polymicrobial sepsis correlates with bacteremia, cytokine expression, and mortality.Ann Surg. 1999 Jul;230(1):95-104. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199907000-00014. Ann Surg. 1999. PMID: 10400042 Free PMC article.
-
Ets-2 and C/EBP-beta are important mediators of ovine trophoblast Kunitz domain protein-1 gene expression in trophoblast.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 27;8:14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-14. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17326832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angel P, Imagawa M, Chiu R, Stein B, Imbra R J, Rahmsdorf H J, Jonat C, Herrlich P, Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987;49:729–739. - PubMed
-
- Arias J, Alperts A S, Brindle P, Claret F X, Smeal T, Karin M, Feramisco J, Montminy M. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature. 1994;370:226–229. - PubMed
-
- Bannister A J, Oehler T, Whilhelm D, Angel P, Kouzarides T. Stimulation of c-Jun activity by CBP:c-Jun residues Ser 63/73 are required for CBP induced stimulation in vivo and CBP binding in vitro. Oncogene. 1995;11:2509–2514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
