The Drosophila esc and E(z) proteins are direct partners in polycomb group-mediated repression
- PMID: 9566901
- PMCID: PMC110661
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2825
The Drosophila esc and E(z) proteins are direct partners in polycomb group-mediated repression
Abstract
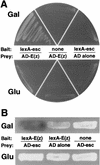
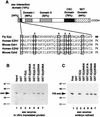
The extra sex combs (esc) and Enhancer of zeste [E(z)] proteins are members of the Drosophila Polycomb group (Pc-G) of transcriptional repressors. Here we present evidence for direct physical interaction between the esc and E(z) proteins using yeast two-hybrid and in vitro binding assays. In addition, coimmunoprecipitation from embryo extracts demonstrates association of esc and E(z) in vivo. We have delimited the esc-binding domain of E(z) to an N-terminal 33-amino-acid region. Furthermore, we demonstrate that site-directed mutations in the esc protein previously shown to impair esc function in vivo disrupt esc-E(z) interactions in vitro. We also show an in vitro interaction between the heed and EZH1 proteins, which are human homologs of esc and E(z), respectively. These results suggest that the esc-E(z) molecular partnership has been conserved in evolution. Previous studies suggested that esc is primarily involved in the early stages of Pc-G-mediated silencing during embryogenesis. However, E(z) is continuously required in order to maintain chromosome binding by other Pc-G proteins. In light of these earlier observations and the molecular data presented here, we discuss how esc-E(z) protein complexes may contribute to transcriptional silencing by the Pc-G.
Figures

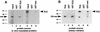
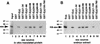


References
-
- Abel K J, Brody L C, Valdes J M, Erdos M R, McKinley D R, Castilla L H, Merajver S D, Couch F J, Friedman L S, Ostermeyer E A, Lynch E D, King M-C, Welcsh P L, Osborne-Lawrence S, Spillman M, Bowcock A M, Collins F S, Weber B L. Characterization of EZH1, a human homolog of Drosophila Enhancer of zeste near BRCA1. Genomics. 1996;37:161–171. - PubMed
-
- Akasaka T, Kanno M, Balling R, Antonio Mieza M, Taniguchi M, Koseki H. A role for mel-18, a Polycomb group-related vertebrate gene, during the anteroposterior specification of the axial skeleton. Development. 1996;122:1513–1522. - PubMed
-
- Alkema M J, Bronk M, Verhoeven E, Otte A, van’t Veer L J, Berns A, van Lohuizen M. Identification of Bmi1-interacting proteins as constituents of a multimeric mammalian Polycomb complex. Genes Dev. 1997;11:226–240. - PubMed
-
- Brunk B P, Martin E C, Adler P N. Drosophila genes Posterior Sex Combs and Suppressor two of zeste encode proteins with homology to the murine bmi-1 oncogene. Nature. 1991;353:351–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
