Interaction of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor signaling proteins with the latent membrane protein 1 PXQXT motif is essential for induction of epidermal growth factor receptor expression
- PMID: 9566902
- PMCID: PMC110662
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2835
Interaction of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor signaling proteins with the latent membrane protein 1 PXQXT motif is essential for induction of epidermal growth factor receptor expression
Abstract
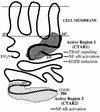
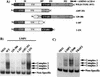
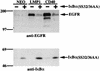
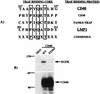
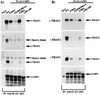
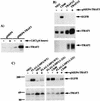
The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) oncoprotein causes multiple cellular changes, including induction of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression and activation of the NF-kappaB transcription factor. LMP1 and the cellular protein CD40, which also induces EGFR expression, interact with the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) proteins. The LMP1 carboxy-terminal activation region 1 signaling domain interacts specifically with the TRAFs and is essential for EGFR induction through a mechanism independent of NF-kappaB alone. LMP1 and CD40 share a common TRAF binding motif, PXQXT. In this study, the PXQXT motifs in both LMP1 and CD40 were altered and mutant proteins were analyzed for induction of EGFR expression. Replacement of the T residue with A in CD40 completely blocked induction of the EGFR, while the same mutation in LMP1 did not affect EGFR induction. Replacement of both P and Q residues with A's in LMP1 reduced EGFR induction by >75%, while deletion of PXQXT blocked EGFR induction. These results genetically link EGFR induction by LMP1 to the TRAF signaling pathway. Overexpression of TRAF2 potently activates NF-kappaB, although TRAF2 did not induce expression of the EGFR either alone or in combination with TRAF1 and TRAF3. In vivo analyses of the interaction of the TRAFs with LMP1 variants mutated in the PXQXT domain indicate that high-level induction of EGFR expression requires interaction with TRAF1, -2, and -3. However, exogenous expression of TRAF3 decreased EGFR induction mediated by either LMP1 or CD40. These data suggest that TRAF-mediated activation of EGFR expression requires assembly of a complex containing the appropriate stoichiometry of TRAF proteins clustered at the cell membrane with LMP1.
Figures

References
-
- Baichwal V R, Sugden B. The multiple membrane-spanning segments of the BNLF-1 oncogene from Epstein-Barr virus are required for transformation. Oncogene. 1989;4:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, de Paoli P, Valle A, Garcia E, Rousset F. Long-term human B cell lines dependent on interleukin-4 and antibody to CD40. Science. 1991;251:70–72. - PubMed
-
- Berberich I, Shu G, Clark E A. Cross-linking CD40 on B-cells rapidly activates nuclear factor-kB. J Immunol. 1994;153:4357–4366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
