Neurexophilins form a conserved family of neuropeptide-like glycoproteins
- PMID: 9570794
- PMCID: PMC6793134
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-10-03630.1998
Neurexophilins form a conserved family of neuropeptide-like glycoproteins
Abstract
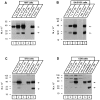
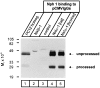
Neurexophilin was discovered as a neuronal glycoprotein that is copurified with neurexin Ialpha during affinity chromatography on immobilized alpha-latrotoxin (Petrenko et al., 1996). We have now investigated how neurexophilin interacts with neurexins, whether it is post-translationally processed by site-specific cleavage similar to neuropeptides, and whether related neuropeptide-like proteins are expressed in brain. Our data show that mammalian brains contain four genes for neurexophilins the products of which share a common structure composed of five domains: an N-terminal signal peptide, a variable N-terminal domain, a highly conserved central domain that is N-glycosylated, a short linker region, and a conserved C-terminal domain that is cysteine-rich. When expressed in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells with a replication-deficient adenovirus, neurexophilin 1 was rapidly N-glycosylated and then slowly processed to a smaller mature form, probably by endoproteolytic cleavage. Similar expression experiments in other neuron-like cells and in fibroblastic cells revealed that N-glycosylation of neurexophilin 1 occurred in all cell types tested, whereas proteolytic processing was observed only in neuron-like cells. Finally, only recombinant neurexin Ialpha and IIIalpha but not neurexin Ibeta interacted with neurexophilin 1 and were preferentially bound to the processed mature form of neurexophilin. Together our data demonstrate that neurexophilins form a family of related glycoproteins that are proteolytically processed after synthesis and bind to alpha-neurexins. The structure and characteristics of neurexophilins indicate that they function as neuropeptides that may signal via alpha-neurexins.
Figures
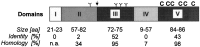



Similar articles
-
Neurexophilin binding to alpha-neurexins. A single LNS domain functions as an independently folding ligand-binding unit.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 25;273(52):34716-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.52.34716. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9856994
-
Structure and evolution of neurexophilin.J Neurosci. 1996 Jul 15;16(14):4360-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-14-04360.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8699246 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of neurexophilin-neurexin complexes reveal a regulatory mechanism of alternative splicing.EMBO J. 2019 Nov 15;38(22):e101603. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101603. Epub 2019 Sep 30. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31566781 Free PMC article.
-
The making of neurexins.J Neurochem. 1998 Oct;71(4):1339-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71041339.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9751164 Review.
-
Alpha-latrotoxin and its receptors CIRL (latrophilin) and neurexin 1 alpha mediate effects on secretion through multiple mechanisms.Biochimie. 2000 May;82(5):447-52. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)00222-4. Biochimie. 2000. PMID: 10865131 Review.
Cited by
-
A stoichiometric complex of neurexins and dystroglycan in brain.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 23;154(2):435-45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105003. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11470830 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexophilin4 is a selectively expressed α-neurexin ligand that modulates specific cerebellar synapses and motor functions.Elife. 2019 Sep 16;8:e46773. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46773. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31524598 Free PMC article.
-
The specific α-neurexin interactor calsyntenin-3 promotes excitatory and inhibitory synapse development.Neuron. 2013 Oct 2;80(1):113-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 24094106 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Investigation of the Malignant Functions and Diagnostic Potential of the Cancer Secretome.Cell Rep. 2019 Mar 5;26(10):2622-2635.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.025. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30840886 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of NXPH4 correlates with poor prognosis, metabolic reprogramming, and immune infiltration in colon adenocarcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;15(2):641-667. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-956. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bravo DA, Gleason JB, Sanchez RI, Roth RA, Fuller RS. Accurate and efficient cleavage of the human insulin proreceptor by the human proprotein-processing protease furin. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:25830–25837. - PubMed
-
- Davletov B, Krasnoperov V, Hata Y, Petrenko AG, Südhof TC. High affinity binding of α-latrotoxin to recombinant neurexin Iα. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23903–23905. - PubMed
-
- Eipper BA, Mains RE. Structure and biosynthesis of pro- adrenocorticotrophin/endorphin and related peptides. Endocr Rev. 1980;1:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M, Ushkaryov YA, Hata Y, Davletov B, Petrenko AG, Südhof TC. Neurexins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:483–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
