Involvement of T cells in enhanced resistance to Klebsiella pneumoniae septicemia in mice treated with liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide phosphatidylethanolamine or gamma interferon
- PMID: 9573076
- PMCID: PMC108150
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.5.1962-1967.1998
Involvement of T cells in enhanced resistance to Klebsiella pneumoniae septicemia in mice treated with liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide phosphatidylethanolamine or gamma interferon
Abstract
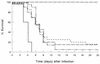
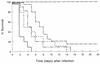
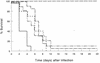
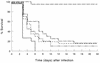
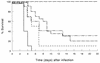
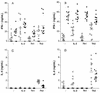
We have previously shown that prophylactic administration of the liposome-encapsulated immunomodulating agents muramyl tripeptide phosphatidylethanolamine (MTPPE) and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) results in strongly increased survival of mice from a normally lethal septicemia with Klebsiella pneumoniae. It was anticipated that the treatment acts on macrophages and nonspecifically augments host resistance to various infections. In the present study, we provide evidence for a key role for T cells in host defense potentiation by the liposomal immunomodulators toward K. pneumoniae septicemia. It is shown that both CD4 and CD8 cells are important in immunomodulation, most likely due to production of IFN-gamma. Depletion of circulating IFN-gamma resulted in strong reduction of the antimicrobial host defense activation. Administration of interleukin-10 resulted in decreased antimicrobial host defense activation by liposomal immunomodulators. Moreover, administration of liposomal immunomodulators was shown to induce predominantly T-helper type 1 (Th1) cell populations in the spleen. These findings indicate that immunomodulation with liposomal MTPPE and IFN-gamma favors Th1 and NK cell activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of nonspecific antimicrobial resistance of mice to Klebsiella pneumoniae septicemia by liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide phosphatidylethanolamine and interferon-gamma alone or combined.J Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;171(2):385-92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.2.385. J Infect Dis. 1995. PMID: 7844375
-
Enhancement of nonspecific resistance by liposome-encapsulated immunomodulators does not affect skin graft rejection in mice.Transplantation. 1995 Dec 15;60(11):1211-4. Transplantation. 1995. PMID: 8525512
-
Treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae septicemia in normal and leukopenic mice by liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide phosphatidylethanolamide.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jan;38(1):147-50. doi: 10.1128/AAC.38.1.147. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994. PMID: 8141571 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic targeting of liposome-encapsulated immunomodulators to macrophages for treatment of cancer metastasis.Immunomethods. 1994 Jun;4(3):273-9. doi: 10.1006/immu.1994.1029. Immunomethods. 1994. PMID: 7820457 Review.
-
Activation of Kupffer cell tumoricidal activity by immunomodulators encapsulated in liposomes.Res Immunol. 1992 Feb;143(2):211-4. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2494(92)80168-k. Res Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1574650 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cytokines and the immunopathology of the spondyloarthropathies.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999 Oct;1(1):67-77. doi: 10.1007/s11926-999-0028-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999. PMID: 11123018 Review.
-
Divergent role of gamma interferon in a murine model of pulmonary versus systemic Klebsiella pneumoniae infection.Infect Immun. 2002 Nov;70(11):6310-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6310-6318.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12379710 Free PMC article.
-
Imunomodulative effect of liposomized muramyltripeptide phosphatidylethanolamine (L-MTP-PE) on mice with alveolar echinococcosis and treated with albendazole.Parasitol Res. 2008 Sep;103(4):919-29. doi: 10.1007/s00436-008-1077-2. Epub 2008 Jun 29. Parasitol Res. 2008. PMID: 18587669
-
Selective regulation of human immunodeficiency virus-infected CD4(+) lymphocytes by a synthetic immunomodulator leads to potent virus suppression in vitro and in hu-PBL-SCID mice.J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(15):6941-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.6941-6952.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11435574 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of immune response elicited by the recombinant outer membrane protein OmpF of Aeromonas hydrophila, a potential vaccine candidate in murine model.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Mar;41(3):1837-48. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3033-9. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24435974
References
-
- Chan S H, Kobayashi M, Santoli D, Perussia B, Tranchieri G. Mechanism of IFN-γ induction by natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF/IL-12) J Immunol. 1992;148:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Chatelain R, Verkila K, Coffman R L. IL-4 induces a Th2 response in Leishmania major-infected mice. J Immunol. 1992;148:1182–1187. - PubMed
-
- Cherwinski H M, Schumacher J H, Brown K D, Mosmann T R. Two types mouse helper T cell clones. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987;166:1229–1244. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cobbold S P, Jayasuriya A, Nash A, Prospero T D, Waldman H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984;312:548–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

