Characterization of the roles of hemolysin and other toxins in enteropathy caused by alpha-hemolytic Escherichia coli linked to human diarrhea
- PMID: 9573087
- PMCID: PMC108161
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.5.2040-2051.1998
Characterization of the roles of hemolysin and other toxins in enteropathy caused by alpha-hemolytic Escherichia coli linked to human diarrhea
Abstract
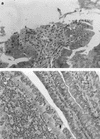
Escherichia coli strains producing alpha-hemolysin have been associated with diarrhea in several studies, but it has not been clearly demonstrated that these strains are enteropathogens or that alpha-hemolysin is an enteric virulence factor. Such strains are generally regarded as avirulent commensals. We examined a collection of diarrhea-associated hemolytic E. coli (DHEC) strains for virulence factors. No strain produced classic enterotoxins, but they all produced an alpha-hemolysin that was indistinguishable from that of uropathogenic E. coli strains. DHEC strains also produced other toxins including cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1) and novel toxins, including a cell-detaching cytotoxin and a toxin that causes HeLa cell elongation. DHEC strains were enteropathogenic in the RITARD (reversible intestinal tie adult rabbit diarrhea) model of diarrhea, causing characteristic enteropathies, including inflammation, necrosis, and colonic cell hyperplasia in both small and large intestines. Alpha-hemolysin appeared to be a major virulence factor in this model since it conferred virulence to nonpathogenic E. coli strains. Other virulence factors also appear to be contributing to virulence. These findings support the epidemiologic link to diarrhea and suggest that further research into the role of DHEC and alpha-hemolysin in enteric disease is warranted.
Figures
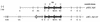
 ,
hly;
░⃞,
cnf.
,
hly;
░⃞,
cnf.


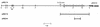
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, et al. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Green Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience; 1987. pp. 2.4.1–2.4.5.
-
- Bankier A T, Weston K M, Barrell B G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxy chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. - PubMed
-
- Benz R, Döbereiner A, Ludwig A, Goebel W. Haemolysin of Escherichia coli: comparison of pore-forming properties between chromosome and plasmid-encoded haemolysins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992;105:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Beutin L. The different haemolysins of Escherichia coli. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1991;180:167–182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

