An rRNA fragment and its antisense can alter decoding of genetic information
- PMID: 9573162
- PMCID: PMC107229
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.10.2744-2748.1998
An rRNA fragment and its antisense can alter decoding of genetic information
Abstract
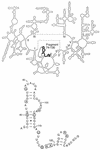
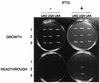
rRNA plays a central role in protein synthesis and is intimately involved in the initiation, elongation, and termination stages of translation. However, the mode of its participation in these reactions, particularly as to the decoding of genetic information, remains elusive. In this paper, we describe a new approach that allowed us to identify an rRNA segment whose function is likely to be related to translation termination. By screening an expression library of random rRNA fragments, we identified a fragment of the Escherichia coli 23S rRNA (nucleotides 74 to 136) whose expression caused readthrough of UGA nonsense mutations in certain codon contexts in vivo. The antisense RNA fragment produced a similar effect, but in neither case was readthrough of UAA or UAG observed. Since termination at UGA in E. coli specifically requires release factor 2 (RF2), our data suggest that the fragments interfere with RF2-dependent termination.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

