Suppressor scanning at positions 177 and 236 in the Escherichia coli lactose/H+ cotransporter and stereotypical effects of acidic substituents that suggest a favored orientation of transmembrane segments relative to the lipid bilayer
- PMID: 9573164
- PMCID: PMC107231
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.10.2756-2758.1998
Suppressor scanning at positions 177 and 236 in the Escherichia coli lactose/H+ cotransporter and stereotypical effects of acidic substituents that suggest a favored orientation of transmembrane segments relative to the lipid bilayer
Abstract
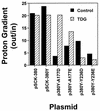
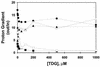
Acidic substituents for Ala-177 (helix 6) or Tyr-236 (helix 7) in LacY cause effects on sugar recognition and cosubstrate coupling that are stereotypical of neutral substituents. Thus, helices 6 and 7 are probably oriented to produce little side-chain contact with the low dielectric lipid bilayer at positions 177 and 236.
Figures
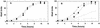
References
-
- Brooker R J. An analysis of lactose permease “sugar specificity” mutations which also affect the coupling between proton and lactose transport. I. Val-177 and Val-177/Asn-319 permeases facilitate proton uniport and sugar uniport. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4131–4138. - PubMed
-
- Brooker R J, Fiebig K, Wilson T H. Characterization of lactose carrier mutants which transport maltose. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:16181–16186. - PubMed
-
- Carrasco N, Antes L M, Poonian M S, Kaback H R. Lac permease of Escherichia coli: histidine-322 and glutamic acid-325 may be components of a charge-relay system. Biochemistry. 1986;25:4486–4488. - PubMed
-
- Gram C D, Brooker R J. An analysis of the side chain requirement at position 177 within the lactose permease which confers the ability to recognize maltose. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3841–3846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

