Nucleotide sequence and spatiotemporal expression of the Vibrio cholerae vieSAB genes during infection
- PMID: 9573178
- PMCID: PMC107168
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.9.2298-2305.1998
Nucleotide sequence and spatiotemporal expression of the Vibrio cholerae vieSAB genes during infection
Abstract
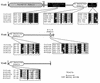
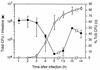
The iviVII gene of Vibrio cholerae was previously identified by a screen for genes induced during intestinal infection. In the present study, nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that iviVII is a 1,659-bp open reading frame, herein designated vieB, that is predicted to be last in a tricistronic operon (vieSAB). The deduced amino acid sequence of VieS exhibited similarity to the sensor kinase component, and those of VieA and VieB were similar to the response regulator components, respectively, of the two-component signal transduction family. Analysis of transcriptional fusions to a site-specific DNA recombinase reporter, tnpR, revealed that vieS and vieA are transcribed during in vitro growth in a vieAB-independent and vieA-dependent manner, respectively. In contrast, transcription of vieB occurred exclusively during infection and was not dependent upon VieB. We conclude that the vieSAB genes are differentially regulated, at least during laboratory growth. Use of a V. cholerae strain harboring a vieB::tnpR transcriptional fusion allowed the kinetics and location of vieB expression within the intestine to be determined. We found that vieB transcription is induced shortly after infection of the proximal and mid-small intestine.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

