The Saccharomyces cerevisiae YCC5 (YCL025c) gene encodes an amino acid permease, Agp1, which transports asparagine and glutamine
- PMID: 9573211
- PMCID: PMC107201
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.9.2556-2559.1998
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae YCC5 (YCL025c) gene encodes an amino acid permease, Agp1, which transports asparagine and glutamine
Abstract
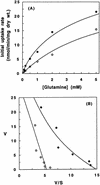
The yeast YCC5 gene encodes a putative amino acid permease and is homologous to GNP1 (encoding a high-affinity glutamine permease). Using strains with disruptions in the genes for multiple permeases, we demonstrated that Ycc5 (which we have renamed Agp1) is involved in the transport of asparagine and glutamine, performed a kinetic analysis of this activity, and showed that AGP1 expression is subject to nitrogen repression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amino acid signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a permease-like sensor of external amino acids and F-Box protein Grr1p are required for transcriptional induction of the AGP1 gene, which encodes a broad-specificity amino acid permease.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):989-1001. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.989. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891035 Free PMC article.
-
GNP1, the high-affinity glutamine permease of S. cerevisiae.Curr Genet. 1996 Jul 31;30(2):107-14. doi: 10.1007/s002940050108. Curr Genet. 1996. PMID: 8660458
-
Cysteine uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae is accomplished by multiple permeases.Curr Genet. 1999 Jul;35(6):609-17. doi: 10.1007/s002940050459. Curr Genet. 1999. PMID: 10467005
-
Nitrogen catabolite repression in yeasts and filamentous fungi.Adv Microb Physiol. 1985;26:1-88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60394-x. Adv Microb Physiol. 1985. PMID: 2869649 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nitrogen regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Gene. 2002 May 15;290(1-2):1-18. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00558-9. Gene. 2002. PMID: 12062797 Review.
Cited by
-
Stp1p, Stp2p and Abf1p are involved in regulation of expression of the amino acid transporter gene BAP3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Feb 15;28(4):974-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.4.974. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10648791 Free PMC article.
-
L-Phenylalanine Transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Participation of GAP1, BAP2, and AGP1.J Amino Acids. 2014;2014:283962. doi: 10.1155/2014/283962. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Amino Acids. 2014. PMID: 24701347 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping of volatile compound production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during alcoholic fermentation.BMC Genomics. 2018 Mar 1;19(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4562-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29490607 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a permease-like sensor of external amino acids and F-Box protein Grr1p are required for transcriptional induction of the AGP1 gene, which encodes a broad-specificity amino acid permease.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):989-1001. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.989. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891035 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional induction by aromatic amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 May;19(5):3360-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.5.3360. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10207060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- André B. An overview of membrane transport proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1995;11:1575–1611. - PubMed
-
- Berben G, Dumont J, Gilliquet V, Bolle P, Hilger F. The YDp plasmids: a uniform set of vectors bearing versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991;7:475–477. - PubMed
-
- Cooper T G. Nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In: Strathern J N, Jones E W, Broach J, editors. The molecular biology of the yeast Saccharomyces: metabolism and gene expression. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1982. pp. 39–99.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

