CD28-B7 costimulatory blockade by CTLA4Ig delays the development of retrovirus-induced murine AIDS
- PMID: 9573306
- PMCID: PMC110124
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.6.5285-5290.1998
CD28-B7 costimulatory blockade by CTLA4Ig delays the development of retrovirus-induced murine AIDS
Abstract
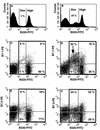
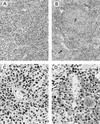
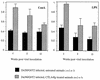
Mouse AIDS (MAIDS) induced in C57BL/6 mice by infection with a replication-defective retrovirus (Du5H) combines extensive lymphoproliferation and profound immunodeficiency. Although B cells are the main target of viral infection, recent research has focused on CD4(+) T cells, the activation of which is a key event in MAIDS induction and progression. A preliminary observation of increased expression of B7 molecules on B cells in MAIDS prompted us to address the possible involvement of the CD28/B7 costimulatory pathway in MAIDS. Mice infected with the MAIDS-inducing viral preparation were treated with murine fusion protein CTLA4Ig (3 x 50 microg/week given intraperitoneally), a competitive inhibitor of physiological CD28-B7 interactions. In CTLA4Ig-treated animals, the onset of the disease was delayed, lymphoproliferation progressed at a much slower rate than in untreated mice, and the loss of in vitro responsiveness to mitogens was reduced. Relative expression of Du5H did not differ between treated and untreated animals. These results suggest that the CD28/B7 costimulatory pathway contributes to MAIDS development.
Figures
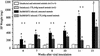

Similar articles
-
Induction of CD4 T cell changes in murine AIDS is dependent on costimulation and involves a dysregulation of homeostasis.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 15;169(2):722-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.722. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12097374
-
Chronic blockade of CD28-B7-mediated T-cell costimulation by CTLA4Ig reduces intimal thickening in MHC class I and II incompatible mouse heart allografts.Transplantation. 1997 Dec 27;64(12):1641-5. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199712270-00002. Transplantation. 1997. PMID: 9422395
-
Control of memory CD4 T cell recall by the CD28/B7 costimulatory pathway.J Immunol. 2006 Dec 1;177(11):7698-706. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.7698. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17114440
-
Targeting the B7/CD28:CTLA-4 costimulatory system in CNS autoimmune disease.J Neuroimmunol. 1998 Aug 14;89(1-2):10-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(98)00058-7. J Neuroimmunol. 1998. PMID: 9726820 Review.
-
The complexity of the B7-CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory pathway.Agents Actions Suppl. 1998;49:33-43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-8857-8_6. Agents Actions Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9426826 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclo-oxygenase type 2-dependent prostaglandin E2 secretion is involved in retrovirus-induced T-cell dysfunction in mice.Biochem J. 2004 Dec 15;384(Pt 3):469-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031859. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15344910 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression in early postnatal days induces persistent and allergen-specific immune tolerance to asthma in adult mice.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 10;10(4):e0122990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122990. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25860995 Free PMC article.
-
CD40-associated TRAF 6 signaling is required for disease induction in a retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(11):6055-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.6055-6060.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15141004 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the CD154-positive and CD40-positive cellular subsets required for pathogenesis in retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3581-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3581-3589.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264347 Free PMC article.
-
The CD154/CD40 interaction required for retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency syndrome is not mediated by upregulation of the CD80/CD86 costimulatory molecules.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(24):13106-10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.24.13106-13110.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12438641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bretscher P. The two-signal model of lymphocyte activation twenty-one years later. Immunol Today. 1992;13:74–76. - PubMed
-
- Champagne E, Scarpellino L, Lane P, Acha-Orbea H. CD28/CTLA4-B7 interaction is dispensable for T cell stimulation by mouse mammary tumor virus superantigen but not for B cell differentiation and virus dissemination. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:1595–1602. - PubMed
-
- Freeman G J, Borriello F, Hodes R J, Reiser H, Gribben J G, Ng J W, Kim J, Goldberg J M, Hathcock K, Laszlo G, Lombard L A, Wang S, Gray G S, Nadler L M, Sharpe A H. Murine B7-2, an alternative CTLA4 counter-receptor that costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1993;178:2185–2192. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

