The N-terminal extension of the influenza B virus nucleoprotein is not required for nuclear accumulation or the expression and replication of a model RNA
- PMID: 9573310
- PMCID: PMC116436
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.6.5307-5312.1998
The N-terminal extension of the influenza B virus nucleoprotein is not required for nuclear accumulation or the expression and replication of a model RNA
Abstract
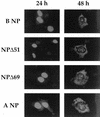
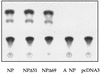
The nucleoprotein (NP) of influenza B virus is 50 amino acids longer at the N-terminus than influenza A virus NP and lacks homology to the A virus protein over the first 69 residues. We have deleted the N-terminal 51 and 69 residues of the influenza B/Ann Arbor/1/66 virus NP and show that nuclear accumulation of the protein is unaffected. This indicates that the nuclear localization signal is not located at the extreme N terminus, as in influenza A virus NP. To determine if the N-terminal mutants could support the expression and replication of a model influenza B virus RNA, the genes encoding the subunits of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (PA, PB1, and PB2) were cloned. Coexpression of NP and the P proteins in 293 cells was found to permit the expression and replication of a transfected model RNA based on segment 4 of B/Maryland/59, in which the hemagglutinin-coding region was replaced by a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene. The expression and replication of the synthetic RNA were not affected by the replacement of NP with NP mutants lacking the N-terminal 51 or 69 residues, indicating that the N-terminal extension is not required for transcription or replication of the viral RNA. In addition, we report that the influenza B virus NP cannot be functionally replaced by type A virus NP in this system.
Figures

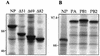


Similar articles
-
The N terminus of the influenza B virus nucleoprotein is essential for virus viability, nuclear localization, and optimal transcription and replication of the viral genome.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12326-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01542-14. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25122787 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of two nuclear localization signals of influenza A virus nucleoprotein to viral replication.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):30-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01434-06. Epub 2006 Oct 18. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17050598 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza virus nucleoprotein interacts with influenza virus polymerase proteins.J Virol. 1998 Jul;72(7):5493-501. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5493-5501.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9621005 Free PMC article.
-
[Structural and Biochemical Analyses on the RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase of Influenza Virus for Development of Novel Anti-influenza Agents].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(2):205-214. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.16-00195. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28154333 Review. Japanese.
-
[Structure and function of influenza virus nucleoprotein (NP)].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Oct;55(10):2599-604. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9360378 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for RNA binding and homo-oligomer formation by influenza B virus nucleoprotein.J Virol. 2012 Jun;86(12):6758-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00073-12. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22496219 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear import of influenza A viral ribonucleoprotein complexes is mediated by two nuclear localization sequences on viral nucleoprotein.Virol J. 2007 Jun 4;4:49. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-49. Virol J. 2007. PMID: 17547769 Free PMC article.
-
A reverse genetics approach for recovery of recombinant influenza B viruses entirely from cDNA.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11744-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11744-11747.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388735 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-dependent N-terminal cleavage of influenza virus nucleocapsid protein in infected cells.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10158-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10158-10163.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559331 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Study of the N-Terminal Region of Influenza B Virus Nucleoprotein.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137802. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26368391 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

