Role of adenosine and its receptors in the vasodilatation induced in the cerebral cortex of the rat by systemic hypoxia
- PMID: 9575299
- PMCID: PMC2230973
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.507bn.x
Role of adenosine and its receptors in the vasodilatation induced in the cerebral cortex of the rat by systemic hypoxia
Abstract
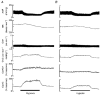
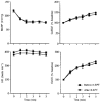
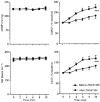
1. In anaesthetized rats, we have examined the role of adenosine in vasodilatation evoked in the cerebral cortex by systemic hypoxia (breathing 8 % O2). Red cell flux was recorded from the surface of the exposed parietal cortex (CoRCF) by a laser Doppler probe, cortical vascular conductance (CoVC) being computed as CoRCF divided by mean arterial blood pressure. All agonists and antagonists were applied topically to the cortex. 2. Systemic hypoxia or adenosine application for 5 or 10 min, respectively, induced an increase in CoRCF and CoVC. These responses were substantially reduced by 8-phenyltheophylline (8-PT), an adenosine receptor antagonist which is non-selective between the adenosine A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. By contrast, the adenosine receptor antagonist 8-sulphophenyltheophylline (8-SPT) which is similarly non-selective, but unlike 8-PT, does not cross the blood-brain barrier, reduced the increases in CoRCF and CoVC induced by adenosine, but had no effect on those induced by hypoxia. 3. The A2A receptor agonist CGS21680 produced a substantial increase in CoRCF and CoVC, but the A1 receptor agonist 2-chloro-N6-cyclopentyladenosine had minimal effects. 4. The A2A receptor antagonist ZM241385 reduced the increase in CoRCF and CoVC induced by adenosine and reduced the increase in CoRCF induced by hypoxia. 5. We propose that exogenous adenosine that is topically applied to the cerebral cortex produces vasodilatation by acting on A2A receptors on the vascular smooth muscle. However, during systemic hypoxia, we propose that adenosine is released from endothelial cells and acts on endothelial A2A receptors to produce the major part of the hypoxia-induced dilatation in the cerebral cortex.
Figures
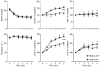



 , CCPA;
, CCPA;  , CGS21680). Values for CoRCF and CoVC during agonist application are shown as percentage of baseline values. ** and * indicate a significant difference between values recorded at baseline and at the 5th minute of agonist application of P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively.
, CGS21680). Values for CoRCF and CoVC during agonist application are shown as percentage of baseline values. ** and * indicate a significant difference between values recorded at baseline and at the 5th minute of agonist application of P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively.
References
-
- Bowton DL, Haddon WS, Prough DS, Adair N, Alford PT, Stump DA. Theophylline effect on the cerebral blood flow response to hypoxemia. Chest. 1988;94:371–375. - PubMed
-
- Bruns RF, Lu GH, Pugsley TA. Characterization of the A2adenosine receptor labelled by [3H]-NECA in rat striatal membranes. Molecular Pharmacology. 1986;29:331–346. - PubMed
-
- Coney A, Marshall JM. Effect of systemic hypoxia upon circulation of the cerebral cortex in the anaesthetized rat. The Journal of Physiology. 1995a;483.P:88. P.
-
- Coney A, Marshall JM. The role of adenosine in cerebral cortical vasodilatation induced by acute systemic hypoxia in normoxic and chronically hypoxic rats under anaesthesia. The Journal of Physiology. 1995b;487.P:174–175. P.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

