Multiple pathways for L-methionine transport in brush-border membrane vesicles from chicken jejunum
- PMID: 9575301
- PMCID: PMC2230979
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.527bn.x
Multiple pathways for L-methionine transport in brush-border membrane vesicles from chicken jejunum
Abstract
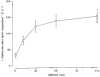
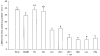
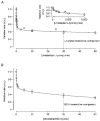
1. The intestinal transport of L-methionine has been investigated in brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from the jejunum of 6-week-old chickens. L-Methionine influx is mediated by passive diffusion and by Na+-dependent and Na+-independent carrier-mediated mechanisms. 2. In the absence of Na+, cis-inhibition experiments with neutral and cationic amino acids indicate that two transport components are involved in L-methionine influx: one sensitive to L-lysine and the other sensitive to 2-aminobicyclo[2.2. 1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH). The L-lysine-sensitive flux is strongly inhibited by L-phenylalanine and can be broken down into two pathways, one sensitive to N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) and the other to L-glutamine and L-cystine. 3. The kinetics of L-methionine influx in Na+-free conditions is described by a model involving three transport systems, here called a, b and c: systems a and b are able to interact with cationic amino acids but differ in their kinetic characteristics (system a: Km = 2.2 +/- 0.3 microM and Vmax = 0.13 +/- 0.005 pmol (mg protein)-1 (2 s)-1; system b: Km = 3.0 +/- 0.3 mM and Vmax = 465 +/- 4.3 pmol (mg protein)-1 (2 s)-1); system c is specific for neutral amino acids, has a Km of 1.29 +/- 0.08 mM and a Vmax of 229 +/- 5.0 pmol (mg protein)-1 (2 s)-1 and is sensitive to BCH inhibition. 4. The Na+-dependent component can be inhibited by BCH and L-phenylalanine but cannot interact either with cationic amino acids or with alpha-(methylamino)isobutyrate (MeAIB). 5. The kinetic analysis of L-methionine influx under a Na+ gradient confirms the activity of the above described transport systems a and b. System a is not affected by the presence of Na+ while system b shows a 3-fold decrease in the Michaelis constant and a 1.4-fold increase in Vmax. In the presence of Na+, the BCH-sensitive component can be subdivided into two pathways: one corresponds to system c and the other is Na+ dependent and has a Km of 0.64 +/- 0. 013 mM and a Vmax of 391 +/- 2.3 pmol (mg protein)-1 (2 s)-1. 6. It is concluded that L-methionine is transported in the chicken jejunum by four transport systems, one with functional characteristics similar to those of system bo, + (system a); a second (system b) similar to system y+, which we suggest naming y+m to account for its high Vmax for L-methionine transport in the absence of Na+; a third (system c) which is Na+ independent and has similar properties to system L; and a fourth showing Na+ dependence and tentatively identified with system B.
Figures

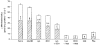


References
-
- Baker DH. Utilization of isomers and analogs of amino acids and other sulfur-containing compounds. Progress in Food and Nutrition Science. 1986;10:133–178. - PubMed
-
- Barker GA, Ellory JC. The identification of neutral amino acid transport systems. Experimental Physiology. 1990;75:3–26. - PubMed
-
- Berteloot A. Characteristics of glutamic acid transport by rabbit intestinal brush border membrane vesicles. Effect of Na+-, K+- and H+-gradients. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1984;775:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Bertran J, Werner A, Moore ML, Stange G, Markovich D, Biber J, Testar X, Zorzano A, Palacín M, Murer H. Expression cloning of a cDNA from rabbit kidney cortex that induces a single transport system for cystine and dibasic and neutral amino acids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1992;89:5601–5605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brachet P, Puigserver A. Na+-independent and nonstereospecific transport of 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutanoic acid by brush border membrane vesicles from chick small intestine. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. 1989;94B:157–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

