Expression pattern of the carrot EP3 endochitinase genes in suspension cultures and in developing seeds
- PMID: 9576773
- PMCID: PMC35020
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.117.1.43
Expression pattern of the carrot EP3 endochitinase genes in suspension cultures and in developing seeds
Abstract
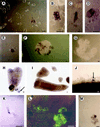
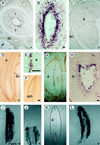
Carrot (Daucus carota) extracellular protein 3 (EP3) class IV endochitinases were previously identified based on their ability to rescue somatic embryos of the temperature-sensitive cell line ts11. Whole-mount in situ hybridization revealed that a subset of the morphologically distinguishable cell types in embryogenic and nonembryogenic suspension cultures, including ts11, express EP3 genes. No expression was found in somatic embryos. In carrot plants EP3 genes are expressed in the inner integumentary cells of young fruits and in a specific subset of cells located in the middle of the endosperm of mature seeds. No expression was found in zygotic embryos. These results support the hypothesis that the EP3 endochitinase has a "nursing" function during zygotic embryogenesis and that this function can be mimicked by suspension cells during somatic embryogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Bewley JD, Black M (1994) Seeds: Physiology of Development and Germination, Ed 2. Plenum Press, New York
-
- Borthwick HA. Development of the macrogametophyte and embryo of Daucus carota. Bot Gaz. 1931;92:23–44.
-
- Bulawa CE, Wasco W. Chitin and nodulation. Nature. 1991;353:710. - PubMed
-
- Cox KH, Goldberg RB. Analysis of plant gene expression. In: Shaw CH, editor. Plant Molecular Biology: A Practical Approach. Oxford, UK: IRL Press; 1988. pp. 1–34.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

