Rhamnogalacturonan alpha-d-galactopyranosyluronohydrolase. An enzyme that specifically removes the terminal nonreducing galacturonosyl residue in rhamnogalacturonan regions of pectin
- PMID: 9576784
- PMCID: PMC34998
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.117.1.153
Rhamnogalacturonan alpha-d-galactopyranosyluronohydrolase. An enzyme that specifically removes the terminal nonreducing galacturonosyl residue in rhamnogalacturonan regions of pectin
Abstract
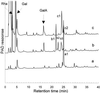
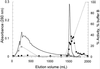
A new enzyme, rhamnogalacturonan (RG) alpha-d-galactopyranosyluronohydrolase (RG-galacturonohydrolase), able to release a galacturonic acid residue from the nonreducing end of RG chains but not from homogalacturonan, was purified from an Aspergillus aculeatus enzyme preparation. RG-galacturonohydrolase acted with inversion of anomeric configuration, initially releasing beta-d-galactopyranosyluronic acid. The enzyme cleaved smaller RG substrates with the highest catalytic efficiency. A Michaelis constant of 85 &mgr;m and a maximum reaction rate of 160 units mg-1 was found toward a linear RG fragment with a degree of polymerization of 6. RG-galacturonohydrolase had a molecular mass of 66 kD, an isoelectric point of 5.12, a pH optimum of 4.0, and a temperature optimum of 50 degreesC. The enzyme was most stable between pH 3.0 and 6.0 (for 24 h at 40 degreesC) and up to 60 degreesC (for 3 h).
Figures




References
-
- Azadi P, O'Neill MA, Bergmann C, Darvill G, Albersheim P. The backbone of the pectic polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan I is cleaved by an endohydrolase and an endolyase. Glycobiology. 1995;5:783–789. - PubMed
-
- Beldman G, Van den Broek LAM, Schols HA, Searle-Van Leeuwen MJF, Van Laere KMJ, Voragen AGJ. An exogalacturonase from Aspergillus aculeatus able to degrade xylogalacturonan. Biotechnol Lett. 1996;18:707–712.
-
- Biely P, Benen J, Heinrichová K, Kester HCM, Visser J. Inversion of configuration during hydrolysis of α-1,4-galacturonidic linkage by three Aspergillus polygalacturonases. FEBS Lett. 1996;382:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Colquhoun IJ, De Ruiter GA, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ. Identification by N.M.R. spectroscopy of oligosaccharides obtained by treatment of the hairy regions of apple pectin with RGase. Carbohydr Res. 1990;206:131–144. - PubMed
-
- De Vries JA, Voragen AGJ, Rombouts FM, Pilnik W. Extraction and purification of pectins from alcohol insoluble solids from ripe and unripe apples. Carbohydr Polym. 1981;1:117–127.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

