Drug resistance of human glioblastoma cells conferred by a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor through modulation of Bcl-XL and caspase-3-like proteases
- PMID: 9576951
- PMCID: PMC20446
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.10.5724
Drug resistance of human glioblastoma cells conferred by a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor through modulation of Bcl-XL and caspase-3-like proteases
Abstract
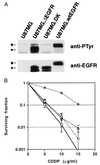
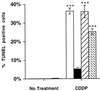
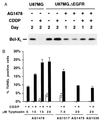
Alterations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene occur frequently in human malignant gliomas. The most common of these is deletion of exons 2-7, resulting in truncation of the extracellular domain (DeltaEGFR or EGFRvIII), which occurs in a large fraction of de novo malignant gliomas (but not in progressive tumors or those lacking p53 function) and enhances tumorigenicity, in part by decreasing apoptosis through up-regulation of Bcl-XL. Here, we demonstrate that the DeltaEGFR concomitantly confers resistance to the chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin (CDDP) by suppression of CDDP-induced apoptosis. Expression of Bcl-XL was elevated in U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells prior to and during CDDP treatment, whereas it decreased considerably in CDDP-treated parental cells. CDDP-induced activation of caspase-3-like proteases was suppressed significantly in U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells. These responses were highly specific to constitutively kinase-active DeltaEGFR, because overexpression of kinase-deficient DeltaEGFR (DK) or wild-type EGFR had no such effects. Correspondingly, DeltaEGFR specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors reduced Bcl-XL expression and potentiated CDDP-induced apoptosis in U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells. Ectopic overexpression of Bcl-XL in parental U87MG cells also resulted in suppression of both caspase activation and apoptosis induced by CDDP. These results may have important clinical implications for the use of CDDP in the treatment of those malignant gliomas expressing DeltaEGFR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A common mutant epidermal growth factor receptor confers enhanced tumorigenicity on human glioblastoma cells by increasing proliferation and reducing apoptosis.Cancer Res. 1996 Nov 1;56(21):5079-86. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8895767
-
Growth suppression of intracranial xenografted glioblastomas overexpressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptors by systemic administration of monoclonal antibody (mAb) 806, a novel monoclonal antibody directed to the receptor.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 15;61(14):5349-54. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11454673
-
Human glioblastoma xenografts overexpressing a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor sensitized to cisplatin by the AG1478 tyrosine kinase inhibitor.J Neurosurg. 2001 Sep;95(3):472-9. doi: 10.3171/jns.2001.95.3.0472. J Neurosurg. 2001. PMID: 11565870
-
Aberrant receptor signaling in human malignant gliomas: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Cancer Lett. 2001 Jan;162 Suppl:S17-S21. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00648-0. Cancer Lett. 2001. PMID: 11164186 Review.
-
The Bcl-xL and Bax-alpha control points: modulation of apoptosis induced by cancer chemotherapy and relation to TPCK-sensitive protease and caspase activation.Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;75(4):301-14. Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9493953 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of magnetic perfusion-weighted imaging to determine epidermal growth factor receptor variant III expression in glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2012 May;14(5):613-23. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos073. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Neuro Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22492960 Free PMC article.
-
Retinamide-induced apoptosis in glioblastomas is associated with down-regulation of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 proteins.J Neurooncol. 2005 Sep;74(3):225-32. doi: 10.1007/s11060-005-7305-z. J Neurooncol. 2005. PMID: 16187019
-
Second Generation mTOR Inhibitors as a Double-Edged Sword in Malignant Glioma Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 10;20(18):4474. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184474. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31510109 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of MKNK2 alternative splicing by splice-switching oligonucleotides as a novel approach for glioblastoma treatment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 30;46(21):11396-11404. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky921. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30329087 Free PMC article.
-
Nimotuzumab enhances temozolomide-induced growth suppression of glioma cells expressing mutant EGFR in vivo.Cancer Med. 2016 Mar;5(3):486-99. doi: 10.1002/cam4.614. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 26778701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fine H A. J Neurooncol. 1994;20:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Feun L G, Savaraj N, Landy H J. J Neurooncol. 1994;20:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Guchelaar H J, Vermes A, Vermes I, Haanen C. Pharm World Sci. 1997;19:119–125. - PubMed
-
- Lowe S W, Bodis S, McClatchey A, Remington L, Ruley H E, Fisher D E, Housman D E, Jacks T. Science. 1994;266:807–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

