Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of ropinirole in parkinsonian patients
- PMID: 9578193
- PMCID: PMC1873962
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.t01-1-00704.x
Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of ropinirole in parkinsonian patients
Abstract
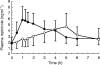
Aims: Ropinirole is a specific non-ergoline dopamine D2-receptor agonist with antiparkinsonian properties. The pharmacokinetic parameters of ropinirole taken in the fasted condition were compared with those when it was co-administered with food.
Methods: This was an open, randomized, two sessions cross over study in 12 patients with Parkinson's disease, comparing the steady-state pharmacokinetic profiles of ropinirole on two different study days: 'fasted' and 'fed'.
Results: The mean Cmax was lower in the 'fed' regimen than in the 'fasted' one (-25%, P=0.002). The median tmax was observed 2.6 h later in the 'fed' regimen than in the 'fasted' regimen (P<0.05). There was a slight but significant decrease in AUC(0,8 h) in the 'fed' regimen (P=0.03).
Conclusions: Food decreases the rate of absorption of ropinirole, but has little effect on the extent of absorption.
Figures
References
-
- Neuvonen PJ, Kivistö KT. The clinical significance of food-drug interactions: a review. Med J Aust. 1989;150:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Vidaihlet M, Bonnet AM, Belal S, Dubois B, Marle C, Agid Y. Ropinirole without levodopa in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 1990;336:316–317. - PubMed
-
- Rascol O, Brooks D, Brunt E, Korczyn A, Poewe W, Stocchi F on behalf of the 056 Study Group. Ropinirole in the treatment of early Parkinson’s disease: a six month interim report of a five year L-dopa control study. Mov Disord. 1997 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical