The beta subunit of the Sec61 complex facilitates cotranslational protein transport and interacts with the signal peptidase during translocation
- PMID: 9585408
- PMCID: PMC2132780
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.4.887
The beta subunit of the Sec61 complex facilitates cotranslational protein transport and interacts with the signal peptidase during translocation
Abstract
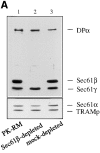
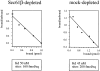
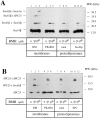
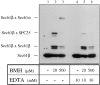
The Sec61 complex is the central component of the protein translocation apparatus of the ER membrane. We have addressed the role of the beta subunit (Sec61beta) during cotranslational protein translocation. With a reconstituted system, we show that a Sec61 complex lacking Sec61beta is essentially inactive when elongation and membrane targeting of a nascent chain occur at the same time. The translocation process is perturbed at a step where the nascent chain would be inserted into the translocation channel. However, if sufficient time is given for the interaction of the nascent polypeptide with the mutant Sec61 complex, translocation is almost normal. Thus Sec61beta kinetically facilitates cotranslational translocation, but is not essential for it. Using chemical cross-linking we show that Sec61beta not only interacts with subunits of the Sec61 complex but also with the 25-kD subunit of the signal peptidase complex (SPC25), thus demonstrating for the first time a tight interaction between the SPC and the Sec61 complex. Interestingly, the cross-links between Sec61beta and SPC25 and between Sec61beta and Sec61alpha depend on the presence of membrane-bound ribosomes, suggesting that these interactions are induced when translocation is initiated. We propose that the SPC is transiently recruited to the translocation site, thus enhancing its activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Binding of ribosomes to the rough endoplasmic reticulum mediated by the Sec61p-complex.J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):925-34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.925. J Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8051212 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cytoplasmic residues of Sec61p involved in ribosome binding and cotranslational translocation.J Cell Biol. 2005 Jan 3;168(1):67-77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200408188. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15631991 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane integration of Sec61alpha: a core component of the endoplasmic reticulum translocation complex.Biochem J. 1998 Apr 1;331 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):161-7. doi: 10.1042/bj3310161. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9512475 Free PMC article.
-
A second signal recognition event required for translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum.Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):167-70. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90301-1. Cell. 1995. PMID: 7628005 Review.
-
Surfing the Sec61 channel: bidirectional protein translocation across the ER membrane.J Cell Sci. 1999 Dec;112 ( Pt 23):4185-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.23.4185. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10564637 Review.
Cited by
-
N-myristoylated c-Abl tyrosine kinase localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum upon binding to an allosteric inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 16;284(42):29005-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.026633. Epub 2009 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19679652 Free PMC article.
-
SPCS1-Dependent E2-p7 processing determines HCV Assembly efficiency.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Feb 7;18(2):e1010310. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010310. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35130329 Free PMC article.
-
The concept of translocational regulation.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jul 28;182(2):225-32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200804157. Epub 2008 Jul 21. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18644895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of discrete sites in Yip1A necessary for regulation of endoplasmic reticulum structure.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054413. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342155 Free PMC article.
-
Yet1p and Yet3p, the yeast homologs of BAP29 and BAP31, interact with the endoplasmic reticulum translocation apparatus and are required for inositol prototrophy.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 11;285(24):18252-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.080382. Epub 2010 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20378542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann R, Bubeck D, Grassucci R, Penczek P, Verschoor A, Blobel G, Frank J. Alignment of conduits for the nascent chain in the ribosome-Sec61 complex. Science. 1997;278:2123–2126. - PubMed
-
- Crowley KS, Reinhart GD, Johnson AE. The signal sequence moves through a ribosomal tunnel into a noncytoplasmic aqueous environment at the ER membrane early in translocation. Cell. 1993;73:1101–1115. - PubMed
-
- Crowley KS, Liao SR, Worrell VE, Reinhart GD, Johnson AE. Secretory proteins move through the endoplasmic reticulum membrane via an aqueous, gated pore. Cell. 1994;78:461–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

