Chlamydomonas kinesin-II-dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons
- PMID: 9585417
- PMCID: PMC2132775
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.4.993
Chlamydomonas kinesin-II-dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons
Abstract
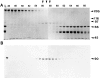
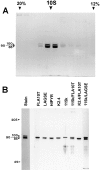
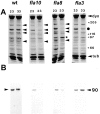
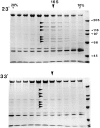
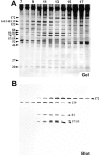
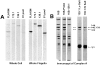
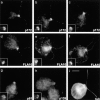
We previously described a kinesin-dependent movement of particles in the flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii called intraflagellar transport (IFT) (Kozminski, K.G., K.A. Johnson, P. Forscher, and J.L. Rosenbaum. 1993. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90:5519-5523). When IFT is inhibited by inactivation of a kinesin, FLA10, in the temperature-sensitive mutant, fla10, existing flagella resorb and new flagella cannot be assembled. We report here that: (a) the IFT-associated FLA10 protein is a subunit of a heterotrimeric kinesin; (b) IFT particles are composed of 15 polypeptides comprising two large complexes; (c) the FLA10 kinesin-II and IFT particle polypeptides, in addition to being found in flagella, are highly concentrated around the flagellar basal bodies; and, (d) mutations affecting homologs of two of the IFT particle polypeptides in Caenorhabditis elegans result in defects in the sensory cilia located on the dendritic processes of sensory neurons. In the accompanying report by Pazour, G.J., C.G. Wilkerson, and G.B. Witman (1998. J. Cell Biol. 141:979-992), a Chlamydomonas mutant (fla14) is described in which only the retrograde transport of IFT particles is disrupted, resulting in assembly-defective flagella filled with an excess of IFT particles. This microtubule- dependent transport process, IFT, defined by mutants in both the anterograde (fla10) and retrograde (fla14) transport of isolable particles, is probably essential for the maintenance and assembly of all eukaryotic motile flagella and nonmotile sensory cilia.
Figures



References
-
- Beech PL, Pagh-Roehl K, Noda Y, Hirokawa N, Burnside B, Rosenbaum JL. Localization of kinesin superfamily proteins to the connecting cilium of fish photoreceptors. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:889–897. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein M, Rosenbaum JL. Kinesin-like proteins in the flagella of Chlamydomonas. . Trends Cell Biol. 1994;4:236–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

