Phosphorylation and association with the transcription factor Atf1 regulate localization of Spc1/Sty1 stress-activated kinase in fission yeast
- PMID: 9585506
- PMCID: PMC316836
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.10.1464
Phosphorylation and association with the transcription factor Atf1 regulate localization of Spc1/Sty1 stress-activated kinase in fission yeast
Abstract
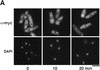
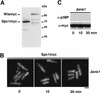
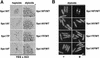
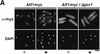
Control of gene expression by stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) cascades is crucial for combating cytotoxic stress. Elements of these cascades have been investigated in detail, but regulation of stress signal transduction from the cytoplasm to the nucleus is poorly understood. Herein are reported subcellular localization studies of fission yeast Spc1, a homolog of human p38 and budding yeast Hog1p SAPKs. Stress induces transient nuclear localization of Spc1. Nuclear translocation of Spc1 is coupled with disassociation from its activator kinase Wis1. However, Spc1 does not concentrate in the nucleus of Deltawis1 cells; therefore Wis1 does not tether Spc1 in the cytoplasm. Unphosphorylatable forms of Spc1 are dispersed in the cytoplasm and nucleus, even in cells that also produce wild-type Spc1. Thus, Spc1 must be phosphorylated by Wis1 to localize in the nucleus. Nuclear retention of Spc1 requires Atf1, a transcription factor that is the key nuclear substrate of Spc1. Nuclear localization of Atf1 requires Pcr1, a heterodimerization partner of Atf1. These studies show that phosphorylation and association with Atf1 are required for nuclear localization of Spc1.
Figures









Comment in
-
SAPKs and transcription factors do the nucleocytoplasmic tango.Genes Dev. 1998 May 15;12(10):1391-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.10.1391. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9585499 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Conjugation, meiosis, and the osmotic stress response are regulated by Spc1 kinase through Atf1 transcription factor in fission yeast.Genes Dev. 1996 Sep 15;10(18):2276-88. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.18.2276. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8824587
-
Regulation of the fission yeast transcription factor Pap1 by oxidative stress: requirement for the nuclear export factor Crm1 (Exportin) and the stress-activated MAP kinase Sty1/Spc1.Genes Dev. 1998 May 15;12(10):1453-63. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.10.1453. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9585505 Free PMC article.
-
Active nucleocytoplasmic shuttling required for function and regulation of stress-activated kinase Spc1/StyI in fission yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 May;10(5):1395-407. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1395. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10233152 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28799013 Review.
-
Nuclear roles and regulation of chromatin structure by the stress-dependent MAP kinase Sty1 of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Nov;82(3):542-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07851.x. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21992435 Review.
Cited by
-
Importin-alpha mediates the regulated nuclear targeting of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase (Sgk) by recognition of a nuclear localization signal in the kinase central domain.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Mar;14(3):1221-39. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-03-0170. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12631736 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of the Fission Yeast Cdc42 Cell-Polarity Module via the Sty1 p38 Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway.Curr Biol. 2016 Nov 7;26(21):2921-2928. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.08.048. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Curr Biol. 2016. PMID: 27746023 Free PMC article.
-
A measurable activation of the bZIP transcription factor Atf1 in a fission yeast strain devoid of stress-activated and cell integrity mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activities.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23434-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C111.338715. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22661707 Free PMC article.
-
Central Roles and Regulatory Mechanisms of Dual-Specificity MAPK Phosphatases in Developmental and Stress Signaling.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 20;9:1697. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01697. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30515185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pheromone-induced nuclear accumulation of the Fus3 MAPK in yeast depends on its phosphorylation state and on Dig1 and Dig2.BMC Cell Biol. 2007 Oct 26;8:44. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-8-44. BMC Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17963515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfa C, Fantes P, Hyams J, McLeod M, Warbrick E. Experiments with fission yeast. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993.
-
- Basi G, Schmid E, Maundrell K. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcription efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene. 1993;123:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Canagarajah BJ, Khokhlatchev A, Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ. Activation mechanism of the MAP kinase ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell. 1997;90:859–869. - PubMed
-
- Cano E, Mahadevan LC. Parallel signal processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
