MMP-9/gelatinase B is a key regulator of growth plate angiogenesis and apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes
- PMID: 9590175
- PMCID: PMC2839071
- DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81169-1
MMP-9/gelatinase B is a key regulator of growth plate angiogenesis and apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes
Abstract
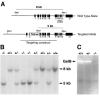
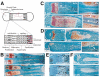
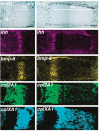
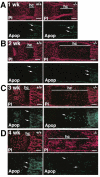
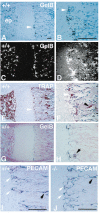
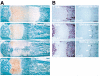
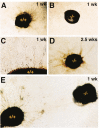
Homozygous mice with a null mutation in the MMP-9/gelatinase B gene exhibit an abnormal pattern of skeletal growth plate vascularization and ossification. Although hypertrophic chondrocytes develop normally, apoptosis, vascularization, and ossification are delayed, resulting in progressive lengthening of the growth plate to about eight times normal. After 3 weeks postnatal, aberrant apoptosis, vascularization, and ossification compensate to remodel the enlarged growth plate and ultimately produce an axial skeleton of normal appearance. Transplantation of wild-type bone marrow cells rescues vascularization and ossification in gelatinase B-null growth plates, indicating that these processes are mediated by gelatinase B-expressing cells of bone marrow origin, designated chondroclasts. Growth plates from gelatinase B-null mice in culture show a delayed release of an angiogenic activator, establishing a role for this proteinase in controlling angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Aharinejad S, Marks SC, Jr., Bock P, MacKay CA, Larson EK, Tahamtani A, Mason-Savas A, Firbas W. Microvascular pattern in the metaphysis during bone growth. Anat. Rec. 1995;242:111–122. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht U, Eichele G, Helms JA, Lu H. Visualization of gene expression patterns by in situ hybridization. In: Daston GP, editor. Molecular and Cellular Methods in Developmental Toxicology. CRC Press; Boca Raton: 1997. pp. 23–48.
-
- Alexander CM, Hansell EJ, Behrendtsen O, Flannery ML, Kishnani NS, Hawkes SP, Werb Z. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development. 1996;122:1723–1736. - PubMed
-
- Alini M, Marriott A, Chen T, Abe S, Poole AR. A novel angiogenic molecule produced at the time of chondrocyte hypertrophy during endochondral bone formation. Dev. Biol. 1996;176:124–132. - PubMed
-
- Amizuka N, Henderson JE, Hoshi K, Warshawsky H, Ozawa H, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC. Programmed cell death of chondrocytes and aberrant chondrogenesis in mice homozygous for parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene deletion. Endocrinology. 1996;137:5055–5067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

