Rapsyn clusters neuronal acetylcholine receptors but is inessential for formation of an interneuronal cholinergic synapse
- PMID: 9592096
- PMCID: PMC6792822
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-11-04166.1998
Rapsyn clusters neuronal acetylcholine receptors but is inessential for formation of an interneuronal cholinergic synapse
Abstract
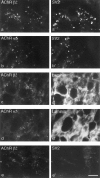
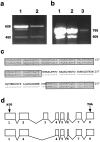
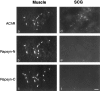
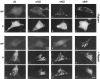
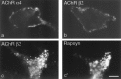
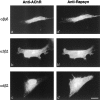
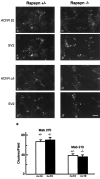
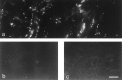
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) are clustered at high density in the postsynaptic membranes of skeletal neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic interneuronal synapses. A cytoplasmic protein, rapsyn, is essential for AChR clustering in muscle. Here, we asked whether rapsyn mediates neuronal AChR clustering at cholinergic synapses in a mammalian sympathetic ganglion, the superior cervical ganglion (SCG). Several observations supported this possibility: (1) AChR clusters containing the alpha3-5 and beta2 subunits, homologs of the muscle AChR subunits, are present at SCG synapses; (2) rapsyn RNA is readily detectable in the SCG; and (3) expression of recombinant rapsyn in heterologous cells induces aggregation of coexpressed neuronal AChR subunits. However, rapsyn protein was undetectable at ganglionic synaptic sites. Moreover, aggregates of neuronal AChRs induced in heterologous cells by full-length rapsyn remained intracellular, whereas rapsyn-induced clusters of muscle AChRs reached the cell surface. Additional studies revealed a second rapsyn RNA species in SCG generated by alternative splicing and competent to encode a novel short rapsyn isoform. However, this isoform clustered neither neuronal nor muscle AChRs in heterologous cells. Most telling, the number, size, and density of AChR clusters in SCG did not differ significantly between neonatal mice bearing a targeted mutation of the rapsyn gene and littermate controls. Thus, rapsyn is dispensable for clustering of ganglionic neuronal nicotinic AChRs.
Figures
References
-
- Apel ED, Roberds SL, Campbell KP, Merlie JP. Rapsyn may function as a link between the acetylcholine receptor and the agrin-binding dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex. Neuron. 1995;15:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Glass DJ, Moscoso LM, Yancopoulos GD, Sanes JR. Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron. 1997;18:623–635. - PubMed
-
- Boulter J, Evans K, Goldman D, Martin G, Treco D, Heinemann S, Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. Nature. 1986;319:368–374. - PubMed
-
- Brakeman PR, Lanahan AA, O’Brien R, Roche K, Barnes CA, Huganir RL, Worley PF. Homer: a protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;386:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Brennan C, Scotland PB, Froehner SC, Henderson LP. Functional properties of acetylcholine receptors coexpressed with the 43K protein in heterologous cell systems. Dev Biol. 1992;149:100–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
