Differentially interconnected networks of GABAergic interneurons in the visual cortex of the cat
- PMID: 9592103
- PMCID: PMC6792813
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-11-04255.1998
Differentially interconnected networks of GABAergic interneurons in the visual cortex of the cat
Abstract
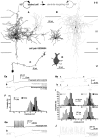
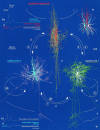
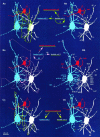
Networks of GABAergic neurons have been implicated in neuronal population synchronization. To define the extent of cellular interconnections, we determined the effect, number, and subcellular distribution of synapses between putative GABAergic neurons in layers II-IV of the cat visual cortex using paired intracellular recordings in vitro followed by correlated light and electron microscopy. All neurons having interneuronal electrophysiological properties were classified by their postsynaptic target profile and were identified as basket (BC; n = 6), dendrite-targeting (DTC; n = 1), and double bouquet (DBC; n = 2) cells. In four out of five anatomically fully recovered and reconstructed cell pairs, synaptic connections were found to be reciprocal. Generally BCs established synaptic junctions closer (21 +/- 20 micron) to postsynaptic somata than did DBCs (43 +/- 19 micron; p < 0.01). The unitary number of synapses (n values, 10, 7, and 20) in each of three BC-to-BC pairs was higher than that in three BC-to-DBC (n values, 1, 2, and 2) and three DBC-to-BC (n values, 1, 4, and 4) connections (p < 0.05). A BC innervated a DTC through two synaptic junctions. Unitary postsynaptic effects mediated by five BCs could be recorded in two BCs, two DBCs, and a DTC. The BCs elicited short-duration fast IPSPs, similar to those mediated by GABAA receptors. At a membrane potential of -55.0 +/- 6.4 mV, unitary IPSPs (n = 5) had a mean amplitude of 919 +/- 863 microV. Postsynaptic response failures were absent when an IPSP was mediated by several release sites. Thus, distinct GABAergic interneurons form reciprocally interconnected networks. The strength of innervation and the proximal placement of synapses suggest a prominent role for BCs in governing the activity of intracortical GABAergic networks in layers II-IV.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fast IPSPs elicited via multiple synaptic release sites by different types of GABAergic neurone in the cat visual cortex.J Physiol. 1997 May 1;500 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):715-38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022054. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9161987 Free PMC article.
-
Effect, number and location of synapses made by single pyramidal cells onto aspiny interneurones of cat visual cortex.J Physiol. 1997 May 1;500 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):689-713. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022053. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9161986 Free PMC article.
-
Massive autaptic self-innervation of GABAergic neurons in cat visual cortex.J Neurosci. 1997 Aug 15;17(16):6352-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-16-06352.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9236244 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface domain specific postsynaptic currents evoked by identified GABAergic neurones in rat hippocampus in vitro.J Physiol. 2000 Apr 1;524 Pt 1(Pt 1):91-116. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-3-00091.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10747186 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic inhibition in the neostriatum.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:91-110. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60006-X. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499110 Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulation of GABAB receptors increases the expression of the proenkephalin gene in slice cultures of rat neocortex.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;367(6):640-7. doi: 10.1007/s00210-003-0746-z. Epub 2003 May 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12732927
-
Tasks for inhibitory interneurons in intact brain circuits.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Jan;88:10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25239808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cornu Ammonis Regions-Antecedents of Cortical Layers?Front Neuroanat. 2017 Sep 26;11:83. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00083. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29018334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local circuits targeting parvalbumin-containing interneurons in layer IV of rat barrel cortex.Brain Struct Funct. 2009 Dec;214(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0225-5. Epub 2009 Oct 31. Brain Struct Funct. 2009. PMID: 19882169 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Interneurons Regulate Temporal Precision and Correlations in Cortical Circuits.Trends Neurosci. 2018 Oct;41(10):689-700. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Trends Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30274604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acsady L, Gorcs TJ, Freund TF. Different populations of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons are specialized to control pyramidal cells or interneurons in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73:317–334. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed B, Anderson JC, Martin KAC, Nelson JC. Map of the synapses onto layer 4 basket cells of the primary visual cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1997;380:230–242. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Eccles JC, Loyning Y. Recurrent inhibition in the hippocampus with identification of the inhibitory cell and its synapses. Nature. 1963;198:540–542. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JC, Douglas RJ, Martin KAC, Nelson JC. Map of the synapses formed with the dendrites of spiny stellate neurons of cat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1994;341:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Avoli M. Inhibitory potentials in neurons of the deep layers of the in vitro neocortical slice. Brain Res. 1986;370:165–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
