Defluorinated sparfloxacin as a new photoproduct identified by liquid chromatography coupled with UV detection and tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 9593143
- PMCID: PMC105763
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.5.1151
Defluorinated sparfloxacin as a new photoproduct identified by liquid chromatography coupled with UV detection and tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
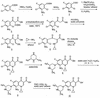
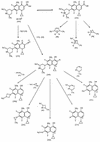
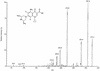
Photodegradation of sparfloxacin was observed by means of high-pressure liquid chromatography with UV detection and liquid chromatography coupled with UV detection and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Three products were detected. Comparison with an independently synthesized derivative of sparfloxacin revealed the structure of one product which is believed to be 8-desfluorosparfloxacin. The second product is likely to be formed by the splitting off of a fluorine and a cyclopropyl ring. Thus, photodefluorination of quinolone antibacterial agents is found and proved for the first time by LC-MS/MS.
Figures






References
-
- Detzer N, Huber B. Photochemie heterocyclischer Enone I, Photolyse und Thermolyse von Nalidixinsäure. Tetrahedron. 1975;31:1937–1941.
-
- Engler M, Holzgrabe U, Kinzig M, Sörgel F. Abstracts of papers of the American Chemical Society. Vol. 211. 1996. Photoproducts of sparfloxacin identified by means of LC-MS/MS; pp. 173–medi. , pt. 2.
-
- Jürgens J, Schedletzky H, Heisig P, Seydel J K, Wiedemann B, Holzgrabe U. Syntheses and biological activities of new N1-aryl substituted quinolone antibacterials. Arch Pharm Med Chem. 1996;329:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Martinez L J, Li G, Chignell C F. Photogeneration of fluoride by the fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents lomefloxacin and fleroxacin. Photochem Photobiol. 1997;65:599–602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

