Flow cytometric assessment of the postantibiotic effect of methicillin on Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 9593149
- PMCID: PMC105776
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.5.1195
Flow cytometric assessment of the postantibiotic effect of methicillin on Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
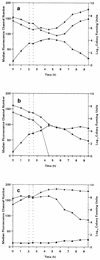
The postantibiotic effect (PAE) following a 2-h exposure of Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 6571 to methicillin (5x the MIC) was investigated with fluorescent probes, 5-cyano-2,3-di-4-tolyl tetrazolium chloride (CTC), an indicator of respiratory activity, and the membrane potential-sensitive compound bis-(1,3-dibutylbarbituric acid) trimethine oxonol [DiBAC4(3)]. Counts of the numbers of CFU on solid agar correlated well with information gained from the CTC and DiBAC4(3) fluorescence intensity distributions obtained by flow cytometry and revealed that the postantibiotic effect was 3.1 h. Due to the capacity of flow cytometry to provide information on the heterogeneity of a bacterial population, both fluorescent probes identified the emergence of an active subpopulation 4 h after removal of the methicillin, indicating the recovery of a small percentage of the population. After removal of the methicillin and resuspension of the cells in methicillin-free medium, a further decrease in the respiratory activity and the membrane integrity of the population was observed, although the CFU counts hardly varied, indicating continued antibiotic-induced damage. Also, CTC fluorescence measurements identified numerous subpopulations during the PAE period; this suggests that the PAE is complex, with individual organisms exhibiting various degrees of recovery. Flow cytometry thus provides a rapid and sensitive alternative to traditional techniques that have been used to study PAE, with the added advantage that physiological changes can be detected as they arise.
Figures

References
-
- Baquero, F., E. Culebras, C. Patron, J. C. Perez-Dias, J. C. Medrano, and M. F. Vicente. 1986. Postantibiotic effect of imipenem on gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 18(Suppl. E):47–59. - PubMed
-
- Bigger J W. The bactericidal action of penicillin on Staphylococcus aureus. Ir J Med Sci. 1944;227:533–568.
-
- Bundtzen R W, Gerber A U, Cohn D, Craig W A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. J Bacteriol. 1981;58:475–490. - PubMed
-
- Craig W A, Vogelman B S. The postantibiotic effect. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:900–902. - PubMed
-
- Craig W A, Gudmundsson S. Postantibiotic effect. In: Lorian V, editor. Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. 4th ed. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1996. pp. 296–329.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

