Regional distribution of interictal 31P metabolic changes in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 9596206
- PMCID: PMC2735262
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01416.x
Regional distribution of interictal 31P metabolic changes in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Purpose: We compared the 31P metabolites in different brain regions of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with those from controls.
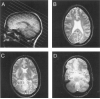
Methods: Ten control subjects and 11 patients with TLE were investigated with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and [31P]MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). [31P]MR spectra were selected from a variety of brain regions inside and outside the temporal lobe.
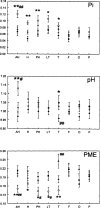
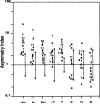
Results: There were no asymmetries of inorganic phosphate (Pi), pH, or phosphomonoesters (PME) between regions in the left and right hemispheres of controls. In patients with TLE, Pi and pH were higher and PME was lower throughout the entire ipsilateral temporal lobe as compared with the contralateral side and there were no significant asymmetries outside the temporal lobe. The degree of ipsilateral/contralateral asymmetry for all three metabolites was substantially greater for the temporal lobe than for the frontal, occipital, and parietal lobes, and these asymmetries provided additional data for seizure localization. As compared with levels in controls, Pi and pH were increased and PME were decreased on the ipsilateral side in patients with TLE. There were changes in Pi, pH, and PME on the contralateral side in persons with epilepsy as compared with controls, contrary to changes on the ipsilateral side.
Conclusions: Our findings provide some insight into the metabolic changes that occur in TLE and may prove useful adjuncts for seizure focus lateralization or localization.
Figures
References
-
- Scheuer ML, Pedley TA. The evaluation and treatment of seizures. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1468–74. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Brown WJ. Pathological findings in epilepsy. In: Engel J Jr, editor. Surgical treatment of the epilepsies. Raven Press; New York: 1987. pp. 511–70.
-
- Jackson GD, Berkovic SF, Tress BM, et al. Hippocampal sclerosis can be reliably detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1990;40:1869–75. - PubMed
-
- Berkovich SF, Andermann F, Ethier R, et al. Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1991;29:175–82. - PubMed
-
- Heinz ER, Crain BJ, Radtke RA, et al. MR Imaging in patients with temporal lobe seizures: correlation of results with pathologic findings. AJR. 1990;155:581–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

