A low concentration of ethanol reduces the chemiluminescence of human granulocytes and monocytes but not the tumor necrosis factor alpha production by monocytes after endotoxin stimulation
- PMID: 9596752
- PMCID: PMC108274
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.6.2809-2813.1998
A low concentration of ethanol reduces the chemiluminescence of human granulocytes and monocytes but not the tumor necrosis factor alpha production by monocytes after endotoxin stimulation
Abstract
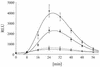
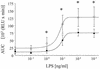
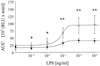
The ability of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and monocytes (Mphi) to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) has been related closely to their potential in the killing of microorganisms. Ethanol has been shown to impair the generation of ROS in these phagocytes after stimulation with some immunogens and to increase the susceptibility of alcohol abusers to infectious diseases. As endotoxemia is common in alcohol abusers, we investigated the effect of ethanol (21.7 mmol/liter) on the luminol-amplified chemiluminescence of PMNs and Mphi after endotoxin stimulation and the release of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) from Mphi. Further, the efficiency of ethanol to inactivate chemically generated ROS was tested. Significant stimulation of ROS release occurred at endotoxin concentrations of 1 ng/ml or higher in both PMNs and Mphi. Ethanol significantly suppressed the formation of ROS in both cell types, the decrease being more pronounced in Mphi (-73. 8%) than in PMNs (-45.7%). The correlations between endotoxin concentration and the amount of released ROS showed a dose-dependent, sigmoidal course. Concentrations of endotoxin necessary for half-maximum stimulation were nearly identical (6 to 8 ng/ml) in both PMNs and Mphi, independent of the presence of ethanol. In contrast to ROS formation, ethanol had no effect on the amount of TNF-alpha produced by endotoxin-stimulated Mphi. Ethanol was shown to be unable to decrease the levels of chemically generated ROS under physiological conditions. Therefore, ethanol cannot be assumed to be an "antioxidative" compound but rather seems to modify processes of endotoxin recognition, intracellular signal transduction, or metabolism.
Figures
References
-
- Adams H G, Jordan C. Infections in the alcoholic. Med Clin North Am. 1984;68:179–200. - PubMed
-
- Aniansson H, Stendahl O, Dahlgren C. Comparison between luminol- and lucigenin-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Sect C. 1984;92:357–361. - PubMed
-
- Babior B M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts) N Engl J Med. 1978;298:721–725. - PubMed
-
- Barth J, Ravens K G. The effect of ethanol on luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of leukocytes. Blutalkohol. 1984;21:464–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

