Pasteurella haemolytica A1-derived leukotoxin and endotoxin induce intracellular calcium elevation in bovine alveolar macrophages by different signaling pathways
- PMID: 9596757
- PMCID: PMC108279
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.6.2836-2844.1998
Pasteurella haemolytica A1-derived leukotoxin and endotoxin induce intracellular calcium elevation in bovine alveolar macrophages by different signaling pathways
Abstract
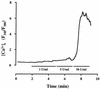
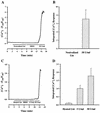
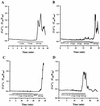
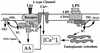
Leukotoxin and endotoxin derived from Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1 are the primary virulence factors contributing to the pathogenesis of lung injury in bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Activation of bovine alveolar macrophages with endotoxin or leukotoxin results in the induction of cytokine gene expression, with different kinetics (H. S. Yoo, S. K. Maheswaran, G. Lin, E. L. Townsend, and T. R. Ames, Infect. Immun. 63:381-388, 1995; H. S. Yoo, B. S. Rajagopal, S. K. Maheswaran, and T. R. Ames, Microb. Pathog. 18:237-252, 1995). Furthermore, extracellular Ca2+ is required for leukotoxin-induced cytokine gene expression. However, the involvement of Ca2+ in endotoxin effects and the precise signaling mechanisms in the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ by leukotoxin and endotoxin are not known. In fura-2-acetoxymethyl ester-loaded alveolar macrophages, intracellular Ca2+ regulation by leukotoxin and endotoxin was studied by video fluorescence microscopy. Leukotoxin induced a sustained elevation of intracellular Ca2+ in a concentration-dependent fashion by influx of extracellular Ca2+ through voltage-gated channels. In the presence of fetal bovine serum, endotoxin elevated intracellular Ca2+ even in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. Leukotoxin-induced intracellular Ca2+ elevation was inhibited by pertussis toxin, inhibitors of phospholipases A2 and C, and the arachidonic acid analog 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid. Intracellular Ca2+ elevation by endotoxin was inhibited by inhibitors of phospholipase C and protein tyrosine kinase, but not by pertussis toxin, or the arachidonic acid analog. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of Ca2+ signaling by leukotoxin through a G-protein-coupled mechanism involving activation of phospholipases A2 and C and release of arachidonic acid in bovine alveolar macrophages. Ca2+ signaling by endotoxin, on the other hand, involves activation of phospholipase C and requires tyrosine phosphorylation. The differences in the Ca2+ signaling mechanisms may underlie the reported temporal differences in gene expression during leukotoxin and endotoxin activation.
Figures
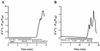




References
-
- Ambs P, Fitzke E, Dieter P. AA-release is under control of PLA2 and DAG lipase in rat liver macrophages. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukotriene Res. 1995;23:81–83. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch G M, Reed P W. Evidence for inhibition of leukotriene A4 synthesis by 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid in guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:4156–4159. - PubMed
-
- Chandra Sekar M, Hokin L E. The role of phosphoinositides in signal transduction. J Membr Biol. 1986;89:193–210. - PubMed
-
- Chang Z L, Novotney M, Suzuki T. Phospholipase C and A2 in tumoricidal activation of murine macrophage-like cell lines. FASEB J. 1990;4:A1753.
-
- Chen T Y, Lei M G, Suzuki T, Morrison D C. Lipopolysaccharide receptors and signal transduction pathways in mononuclear phagocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181:169–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

