Acute and chronic phases of Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice modulate the host immune responses
- PMID: 9596779
- PMCID: PMC108301
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.6.2991-2995.1998
Acute and chronic phases of Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice modulate the host immune responses
Abstract
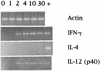
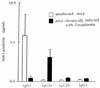
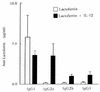
Murine antibody responses to soluble proteins are generally restricted to the immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) isotype. When mice were infected with Toxoplasma gondii Beverley and concomitantly immunized with a soluble unrelated protein antigen, a modification in the isotypic distribution of antibodies directed against this nonparasite antigen was observed, with a preferential production of IgG2a. Interestingly, when mice were immunized with a soluble protein antigen during the chronic phase (day 40) of infection with T. gondii Beverley, a similar modification in the isotypic distribution of antiprotein antibodies was observed.
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Wahab R M, Morsy T A, Abdel-Rahim M I, Essa M H, Al-Alfy Y E. The histopathological picture of concomitant infection with Leishmania major and Toxoplasma gondii in albino mice. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 1989;19:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Afonso L C C, Scharton T M, Vieira L Q, Wysocka M, Trichieri G, Scott P. The adjuvant effect of interleukin-12 in a vaccine against Leishmania major. Science. 1994;263:235–237. - PubMed
-
- Albright J W, Holmes K L, Albright J F. Fluctuations in subsets of splenocytes and isotypes of Ig in young adult and aged mice resulting from Trypanosoma musculi infections. J Immunol. 1990;144:3970–3979. - PubMed
-
- Beverley J K A. Congenital transmission of toxoplasmosis through successive generations of mice. Nature (London) 1959;183:1348–1350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

