Assessing sequence comparison methods with reliable structurally identified distant evolutionary relationships
- PMID: 9600919
- PMCID: PMC27587
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6073
Assessing sequence comparison methods with reliable structurally identified distant evolutionary relationships
Abstract
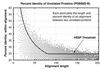
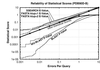
Pairwise sequence comparison methods have been assessed using proteins whose relationships are known reliably from their structures and functions, as described in the SCOP database [Murzin, A. G., Brenner, S. E., Hubbard, T. & Chothia C. (1995) J. Mol. Biol. 247, 536-540]. The evaluation tested the programs BLAST [Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W. & Lipman, D. J. (1990). J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403-410], WU-BLAST2 [Altschul, S. F. & Gish, W. (1996) Methods Enzymol. 266, 460-480], FASTA [Pearson, W. R. & Lipman, D. J. (1988) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 2444-2448], and SSEARCH [Smith, T. F. & Waterman, M. S. (1981) J. Mol. Biol. 147, 195-197] and their scoring schemes. The error rate of all algorithms is greatly reduced by using statistical scores to evaluate matches rather than percentage identity or raw scores. The E-value statistical scores of SSEARCH and FASTA are reliable: the number of false positives found in our tests agrees well with the scores reported. However, the P-values reported by BLAST and WU-BLAST2 exaggerate significance by orders of magnitude. SSEARCH, FASTA ktup = 1, and WU-BLAST2 perform best, and they are capable of detecting almost all relationships between proteins whose sequence identities are >30%. For more distantly related proteins, they do much less well; only one-half of the relationships between proteins with 20-30% identity are found. Because many homologs have low sequence similarity, most distant relationships cannot be detected by any pairwise comparison method; however, those which are identified may be used with confidence.
Figures
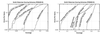



References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W. Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:460–480. - PubMed
-
- Murzin A G, Brenner S E, Hubbard T, Chothia C. J Mol Biol. 1995;247:536–540. - PubMed
-
- Brenner S E, Chothia C, Hubbard T J P, Murzin A G. Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:635–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

