Vitamin B2-based blue-light photoreceptors in the retinohypothalamic tract as the photoactive pigments for setting the circadian clock in mammals
- PMID: 9600923
- PMCID: PMC27591
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6097
Vitamin B2-based blue-light photoreceptors in the retinohypothalamic tract as the photoactive pigments for setting the circadian clock in mammals
Abstract
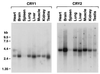
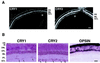
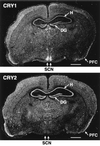
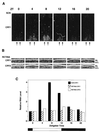
In mammals the retina contains photoactive molecules responsible for both vision and circadian photoresponse systems. Opsins, which are located in rods and cones, are the pigments for vision but it is not known whether they play a role in circadian regulation. A subset of retinal ganglion cells with direct projections to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) are at the origin of the retinohypothalamic tract that transmits the light signal to the master circadian clock in the SCN. However, the ganglion cells are not known to contain rhodopsin or other opsins that may function as photoreceptors. We have found that the two blue-light photoreceptors, cryptochromes 1 and 2 (CRY1 and CRY2), recently discovered in mammals are specifically expressed in the ganglion cell and inner nuclear layers of the mouse retina. In addition, CRY1 is expressed at high level in the SCN and oscillates in this tissue in a circadian manner. These data, in conjunction with the established role of CRY2 in photoperiodism in plants, lead us to propose that mammals have a vitamin A-based photopigment (opsin) for vision and a vitamin B2-based pigment (cryptochrome) for entrainment of the circadian clock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cryptochrome: the second photoactive pigment in the eye and its role in circadian photoreception.Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:31-67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.31. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10966452 Review.
-
Melanopsin: a novel photopigment involved in the photoentrainment of the brain's biological clock?Ann Med. 2002;34(5):401-7. doi: 10.1080/078538902320772151. Ann Med. 2002. PMID: 12452484 Review.
-
Circadian photoreception in humans and mice.Mol Interv. 2002 Dec;2(8):484-92. doi: 10.1124/mi.2.8.484. Mol Interv. 2002. PMID: 14993400 Review.
-
Cryptochromes and inner retinal non-visual irradiance detection.Novartis Found Symp. 2003;253:31-42; discussion 42-55, 102-9, 281-4. Novartis Found Symp. 2003. PMID: 14712913
-
Three vitamins are involved in regulation of the circadian rhythm.Nutr Rev. 2002 Aug;60(8):257-60. doi: 10.1301/002966402320289386. Nutr Rev. 2002. PMID: 12199301 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and function of photolyase and in vivo enzymology: 50th anniversary.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 21;283(47):32153-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800052200. Epub 2008 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18682397 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Hypothesis on the Role of Cryptochromes in Inflammation and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Outcome.Front Neurol. 2017 Nov 28;8:637. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00637. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29234304 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular location and circadian rhythm of expression of the biological clock gene Period 1 in the mouse retina.J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 20;23(20):7670-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-20-07670.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12930806 Free PMC article.
-
A Nobel-Winning Scientist: Aziz Sancar and the Impact of his Work on the Molecular Pathology of Neoplastic Diseases.Turk Patoloji Derg. 2021;37(2):93-105. doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2020.01504. Turk Patoloji Derg. 2021. PMID: 33973640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of photoregulated gene expression in marine diatoms.Plant Mol Biol. 1999 Aug;40(6):1031-44. doi: 10.1023/a:1006256300969. Plant Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10527427
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

