Visualization of elongation factor G on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: the mechanism of translocation
- PMID: 9600930
- PMCID: PMC27598
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6134
Visualization of elongation factor G on the Escherichia coli 70S ribosome: the mechanism of translocation
Abstract
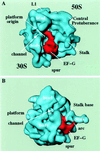
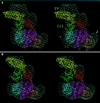
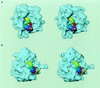
During protein synthesis, elongation factor G (EF-G) binds to the ribosome and promotes the step of translocation, a process in which tRNA moves from the A to the P site of the ribosome and the mRNA is advanced by one codon. By using three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy, we have visualized EF-G in a ribosome-EF-G-GDP-fusidic acid complex. Fitting the crystal structure of EF-G-GDP into the cryo density map reveals a large conformational change mainly associated with domain IV, the domain that mimics the shape of the anticodon arm of the tRNA in the structurally homologous ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. The tip portion of this domain is found in a position that overlaps the anticodon arm of the A-site tRNA, whose position in the ribosome is known from a study of the pretranslocational complex, implying that EF-G displaces the A-site tRNA to the P site by physical interaction with the anticodon arm.
Figures
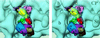
Comment in
-
Form follows function: structure of an elongation factor G-ribosome complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 23;95(13):7237-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7237. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9636131 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

