Efficient construction of a large nonimmune phage antibody library: the production of high-affinity human single-chain antibodies to protein antigens
- PMID: 9600934
- PMCID: PMC27609
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6157
Efficient construction of a large nonimmune phage antibody library: the production of high-affinity human single-chain antibodies to protein antigens
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999 Jan 19;96(2):795. Lindqvist E [corrected to Lindquist E]
Abstract
A large library of phage-displayed human single-chain Fv antibodies (scFv), containing 6.7 x 10(9) members, was generated by improving the steps of library construction. Fourteen different protein antigens were used to affinity select antibodies from this library. A panel of specific antibodies was isolated with each antigen, and each panel contained an average of 8.7 different scFv. Measurements of antibody-antigen interactions revealed several affinities below 1 nM, comparable to affinities observed during the secondary murine immune response. In particular, four different scFv recognizing the ErbB2 protein had affinities ranging from 220 pM to 4 nM. Antibodies derived from the library proved to be useful reagents for immunoassays. For example, antibodies generated to the Chlamydia trachomatis elementary bodies stained Chlamydia-infected cells, but not uninfected cells. These results demonstrate that phage antibody libraries are ideally suited for the rapid production of panels of high-affinity mAbs to a wide variety of protein antigens. Such libraries should prove especially useful for generating reagents to study the function of gene products identified by genome projects.
Figures
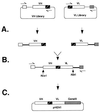
 and an equimolar mixture of HuJH primers
and an equimolar mixture of HuJH primers  . The linker DNA and VL genes were amplified by using a plasmid specific primer
. The linker DNA and VL genes were amplified by using a plasmid specific primer  and an equimolar mixture of RHuJH primers
and an equimolar mixture of RHuJH primers  . The RHuJH primers are complementary to the HuJH primers. (B) The VH and linker DNA-VL gene repertoires were PCR assembled into a scFv gene repertoire. (C) The assembled scFv gene repertoire was cut with the restriction enzymes NcoI and NotI and cloned into the plasmid pHEN1 (17) for phage display.
. The RHuJH primers are complementary to the HuJH primers. (B) The VH and linker DNA-VL gene repertoires were PCR assembled into a scFv gene repertoire. (C) The assembled scFv gene repertoire was cut with the restriction enzymes NcoI and NotI and cloned into the plasmid pHEN1 (17) for phage display.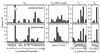
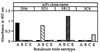
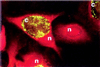
References
-
- Marks J D, Hoogenboom H R, Griffiths A D, Winter G. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16007–16010. - PubMed
-
- Winter G, Griffiths A D, Hawkins R E, Hoogenboom H R. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:433–455. - PubMed
-
- Marks C, Marks J D. N Eng J Med. 1996;335:730–733. - PubMed
-
- Pastan I, Pai L H, Brinkmann U, Fitzgerald D. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;38:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

