Transcytosis of alpha1-acidic glycoprotein in the continuous microvascular endothelium
- PMID: 9600937
- PMCID: PMC27616
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6175
Transcytosis of alpha1-acidic glycoprotein in the continuous microvascular endothelium
Abstract
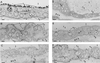
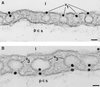
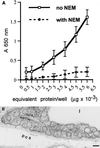
By using perfusions and bolus administration, coupled with postembedding immunocytochemical procedures, we have identified the structures involved in the transport of derivatized orosomucoid (alpha1-acidic glycoprotein) across the continuous microvascular endothelium of the murine myocardium. Our findings indicate that: (i) monomeric orosomucoid binds to the luminal surface of the endothelium; (ii) it is restricted to caveolae during its transport across the endothelium; (iii) it is detected in the perivascular spaces at early time points (by 1 min) and in larger quantities at later time points (>5 min) from the beginning of its perfusion or its intravascular administration; (iv) no orosomucoid molecules are found in the intercellular junctions or at the abluminal exits of interendothelial spaces; and (v) the vesicular transport of orosomucoid is strongly inhibited by N-ethylmaleimide (>80%). Because, by size and shape, the orosomucoid qualifies as a preferential probe for the postulated small pore system, our results are discussed in relation to the pore theory of capillary permeability.
Figures

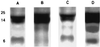
References
-
- McPherson A, Friedman M L, Halsall H B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;124:619–624. - PubMed
-
- Schmid K. In: The Plasma Proteins. Putnam F W, editor. Vol. 1. San Francisco: Academic; 1975. pp. 183–229.
-
- Schmid K. In: Alpha1-Acid Glycoprotein: Genetics, Biochemistry, Physiological Functions and Pharmacology. Baumann P, Müller W E, Eap C B, Tillement J-P, editors. New York: Liss; 1989. pp. 7–22.
-
- Haraldsson B. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985;123:427–436. - PubMed
-
- Haraldsson B, Ripe B. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987;129:127–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

