CIITA stimulation of transcription factor binding to major histocompatibility complex class II and associated promoters in vivo
- PMID: 9600954
- PMCID: PMC27653
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6267
CIITA stimulation of transcription factor binding to major histocompatibility complex class II and associated promoters in vivo
Abstract
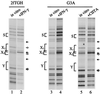
CIITA is a master transactivator of the major histocompatibility complex class II genes, which are involved in antigen presentation. Defects in CIITA result in fatal immunodeficiencies. CIITA activation is also the control point for the induction of major histocompatibility complex class II and associated genes by interferon-gamma, but CIITA does not bind directly to DNA. Expression of CIITA in G3A cells, which lack endogenous CIITA, followed by in vivo genomic footprinting, now reveals that CIITA is required for the assembly of transcription factor complexes on the promoters of this gene family, including DRA, Ii, and DMB. CIITA-dependent promoter assembly occurs in interferon-gamma-inducible cell types, but not in B lymphocytes. Dissection of the CIITA protein indicates that transactivation and promoter loading are inseparable and reveal a requirement for a GTP binding motif. These findings suggest that CIITA may be a new class of transactivator.
Figures

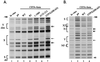

Similar articles
-
CIITA-induced occupation of MHC class II promoters is independent of the cooperative stabilization of the promoter-bound multi-protein complexes.Int Immunol. 1999 Mar;11(3):461-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.3.461. Int Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10221658
-
Malignant glioma cells use MHC class II transactivator (CIITA) promoters III and IV to direct IFN-gamma-inducible CIITA expression and can function as nonprofessional antigen presenting cells in endocytic processing and CD4(+) T-cell activation.Glia. 2001 Dec;36(3):391-405. doi: 10.1002/glia.1125. Glia. 2001. PMID: 11746775
-
Expression of the MHC class II transactivator (CIITA) type IV promoter in B lymphocytes and regulation by IFN-gamma.Mol Immunol. 2006 Feb;43(6):519-28. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.05.005. Epub 2005 Jun 13. Mol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 15950283 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-review: Specificity and expression of CIITA, the master regulator of MHC class II genes.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Jun;34(6):1513-25. doi: 10.1002/eji.200424964. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15162420 Review.
-
Expression of MHC II genes.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;290:147-70. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26363-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16480042 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional scaffold: CIITA interacts with NF-Y, RFX, and CREB to cause stereospecific regulation of the class II major histocompatibility complex promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;20(16):6051-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.16.6051-6061.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10913187 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired regulation of HLA-DR expression in human immunodeficiency virus-infected monocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 Jul;9(4):739-46. doi: 10.1128/cdli.9.4.739-746.2002. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12093667 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Bordetella pertussis infection of primary human monocytes alters HLA-DR expression.Infect Immun. 2004 Mar;72(3):1450-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1450-1462.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14977950 Free PMC article.
-
Class II transactivator: mastering the art of major histocompatibility complex expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(17):6185-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.17.6185-6194.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10938095 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
NLRC5: a newly discovered MHC class I transactivator (CITA).Microbes Infect. 2012 Jun;14(6):477-84. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.12.007. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22209772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwartz R H. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. - PubMed
-
- Steimle V, Otten L A, Zufferey M, Mach B. Cell. 1993;75:135–146. - PubMed
-
- Chin K-C, Mao C, Skinner C, Riley J L, Wright K L, Moreno C S, Stark G R, Boss J M, Ting J P-Y. Immunity. 1994;1:687–697. - PubMed
-
- Steimle V, Siegrist C A, Mottet A, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Mach B. Science. 1994;265:106–109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

