Continuous amperometric monitoring of glucose in a brittle diabetic chimpanzee with a miniature subcutaneous electrode
- PMID: 9600973
- PMCID: PMC27726
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6379
Continuous amperometric monitoring of glucose in a brittle diabetic chimpanzee with a miniature subcutaneous electrode
Abstract
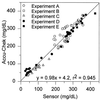
The performance of an amperometric biosensor, consisting of a subcutaneously implanted miniature (0.29 mm diameter, 5 x 10(-4) cm2 mass transporting area), 90 s 10-90% rise/decay time glucose electrode, and an on-the-skin electrocardiogram Ag/AgCl electrode was tested in an unconstrained, naturally diabetic, brittle, type I, insulin-dependent chimpanzee. The chimpanzee was trained to wear on her wrist a small electronic package and to present her heel for capillary blood samples. In five sets of measurements, averaging 5 h each, 82 capillary blood samples were assayed, their concentrations ranging from 35 to 400 mg/dl. The current readings were translated to blood glucose concentration by assaying, at t = 1 h, one blood sample for each implanted sensor. The rms error in the correlation between the sensor-measured glucose concentration and that in capillary blood was 17.2%, 4.9% above the intrinsic 12.3% rms error of the Accu-Chek II reference, through which the illness of the chimpanzee was routinely managed. Linear regression analysis of the data points taken at t>1 h yielded the relationship (Accu-Chek) = 0. 98 x (implanted sensor) + 4.2 mg/dl, r2 = 0.94. The capillary blood and the subcutaneous glucose concentrations were statistically indistinguishable when the rate of change was less than 1 mg/(dl. min). However, when the rate of decline exceeded 1.8 mg/(dl.min) after insulin injection, the subcutaneous glucose concentration was transiently higher.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold M A. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1996;7:46–49. - PubMed
-
- Spanner G, Niessner R. Fresenius’ J Anal Chem. 1996;355:327–328. - PubMed
-
- Berger A J, Itzkan I, Feld M S. Spectrochim Acta, Part A. 1997;53:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Heise H M. Horm Metab Res. 1996;28:527–534. - PubMed
-
- Kohl M, Essenpreis M, Cope M. Phys Med Biol. 1995;40:1267–1287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

