Identification of rat susceptibility loci for adjuvant-oil-induced arthritis
- PMID: 9600974
- PMCID: PMC27729
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6383
Identification of rat susceptibility loci for adjuvant-oil-induced arthritis
Abstract
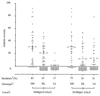
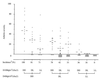
One intradermal injection of incomplete Freund's adjuvant-oil induces a T cell-mediated inflammatory joint disease in DA rats. Susceptibility genes for oil-induced arthritis (OIA) are located both within and outside the major histocompatibility complex (MHC, Oia1). We have searched for disease-linked non-MHC loci in an F2 intercross between DA rats and MHC-identical but arthritis-resistant LEW.1AV1 rats. A genome-wide scan with microsatellite markers revealed two major chromosome regions that control disease incidence and severity: Oia2 on chromosome 4 (P = 4 x 10(-13)) and Oia3 on chromosome 10 (P = 1 x 10(-6)). All animals homozygous for DA alleles at both loci developed severe arthritis, whereas all those homozygous for LEW.1AV1 alleles were resistant. These results have general implications for situations where nonspecific activation of the immune system (e.g., incomplete Freund's adjuvant-oil) causes inflammation and disease, either alone or in conjunction with specific antigens. They may also provide clues to the etiology of inflammatory diseases in humans, including rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

