Increased rates of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocyte turnover in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques
- PMID: 9600975
- PMCID: PMC27734
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6388
Increased rates of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocyte turnover in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques
Abstract
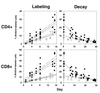
Defining the rate at which T cells turn over has important implications for our understanding of T lymphocyte homeostasis and AIDS pathogenesis, yet little information on T cell turnover is available. We used the nucleoside analogue bromodeoxyuridine (BrdUrd) in combination with five-color flow cytometric analysis to evaluate T lymphocyte turnover rates in normal and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected rhesus macaques. T cells in normal animals turned over at relatively rapid rates, with memory cells turning over more quickly than naive cells. In SIV-infected animals, the labeling and elimination rates of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) BrdUrd-labeled cells were increased by 2- to 3-fold as compared with normal controls. In normal and SIV-infected animals, the rates of CD4(+) T cell BrdUrd-labeling and decay were closely correlated with those of CD8(+) T cells. The elimination rate of BrdUrd-labeled cells was accelerated in both naive and memory T lymphocytes in SIV-infected animals. Our results provide direct evidence for increased rates of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell turnover in AIDS virus infection and have important implications for our understanding of T cell homeostasis and the mechanisms responsible for CD4(+) T cell depletion in AIDS.
Figures

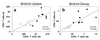
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

