t(11;22)(q23;q11.2) In acute myeloid leukemia of infant twins fuses MLL with hCDCrel, a cell division cycle gene in the genomic region of deletion in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes
- PMID: 9600980
- PMCID: PMC27754
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6413
t(11;22)(q23;q11.2) In acute myeloid leukemia of infant twins fuses MLL with hCDCrel, a cell division cycle gene in the genomic region of deletion in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998 Aug 18;95(17):10344
Abstract
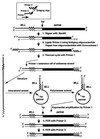
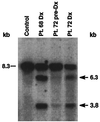
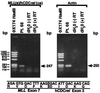
We examined the MLL genomic translocation breakpoint in acute myeloid leukemia of infant twins. Southern blot analysis in both cases showed two identical MLL gene rearrangements indicating chromosomal translocation. The rearrangements were detectable in the second twin before signs of clinical disease and the intensity relative to the normal fragment indicated that the translocation was not constitutional. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with an MLL-specific probe and karyotype analyses suggested t(11;22)(q23;q11. 2) disrupting MLL. Known 5' sequence from MLL but unknown 3' sequence from chromosome band 22q11.2 formed the breakpoint junction on the der(11) chromosome. We used panhandle variant PCR to clone the translocation breakpoint. By ligating a single-stranded oligonucleotide that was homologous to known 5' MLL genomic sequence to the 5' ends of BamHI-digested DNA through a bridging oligonucleotide, we formed the stem-loop template for panhandle variant PCR which yielded products of 3.9 kb. The MLL genomic breakpoint was in intron 7. The sequence of the partner DNA from band 22q11.2 was identical to the hCDCrel (human cell division cycle related) gene that maps to the region commonly deleted in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes. Both MLL and hCDCrel contained homologous CT, TTTGTG, and GAA sequences within a few base pairs of their respective breakpoints, which may have been important in uniting these two genes by translocation. Reverse transcriptase-PCR amplified an in-frame fusion of MLL exon 7 to hCDCrel exon 3, indicating that an MLL-hCDCrel chimeric mRNA had been transcribed. Panhandle variant PCR is a powerful strategy for cloning translocation breakpoints where the partner gene is undetermined. This application of the method identified a region of chromosome band 22q11.2 involved in both leukemia and a constitutional disorder.
Figures

References
-
- Gurney J G, Severson R K, Davis S, Robison L L. Cancer. 1995;75:2186–2195. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:121–125. - PubMed
-
- Clarkson B D, Boyse E A. Lancet. 1971;1:699–701. - PubMed
-
- Zueler W W, Cox D E. Semin Hematol. 1969;6:228–249. - PubMed
-
- Buckley J, Buckley C, Breslow N, Draper G, Roberson P, Mack T. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996;26:223–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

