Molecular characterization of the phenylacetic acid catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida U: the phenylacetyl-CoA catabolon
- PMID: 9600981
- PMCID: PMC27761
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6419
Molecular characterization of the phenylacetic acid catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida U: the phenylacetyl-CoA catabolon
Abstract
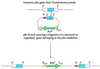
Fourteen different genes included in a DNA fragment of 18 kb are involved in the aerobic degradation of phenylacetic acid by Pseudomonas putida U. This catabolic pathway appears to be organized in three contiguous operons that contain the following functional units: (i) a transport system, (ii) a phenylacetic acid activating enzyme, (iii) a ring-hydroxylation complex, (iv) a ring-opening protein, (v) a beta-oxidation-like system, and (vi) two regulatory genes. This pathway constitutes the common part (core) of a complex functional unit (catabolon) integrated by several routes that catalyze the transformation of structurally related molecules into a common intermediate (phenylacetyl-CoA).
Figures
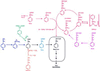



Similar articles
-
Phenylacetyl-coenzyme A is the true inducer of the phenylacetic acid catabolism pathway in Pseudomonas putida U.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Oct;66(10):4575-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.10.4575-4578.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11010921 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic catabolism of phenylacetic acid in Pseudomonas putida U: biochemical characterization of a specific phenylacetic acid transport system and formal demonstration that phenylacetyl-coenzyme A is a catabolic intermediate.J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(24):7667-76. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.24.7667-7676.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8002592 Free PMC article.
-
Catabolism of phenylacetic acid in Escherichia coli. Characterization of a new aerobic hybrid pathway.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25974-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.40.25974. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9748275
-
Regulation of phenylacetic acid uptake is σ54 dependent in Pseudomonas putida CA-3.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Oct 13;11:229. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-229. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21995721 Free PMC article.
-
The phenylacetyl-CoA catabolon: a complex catabolic unit with broad biotechnological applications.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(6):1434-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02344.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11260461 Review.
Cited by
-
Taxis of Pseudomonas putida F1 toward phenylacetic acid is mediated by the energy taxis receptor Aer2.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Apr;79(7):2416-23. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03895-12. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23377939 Free PMC article.
-
Novel phacB-encoded cytochrome P450 monooxygenase from Aspergillus nidulans with 3-hydroxyphenylacetate 6-hydroxylase and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate 6-hydroxylase activities.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Mar;6(3):514-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.00226-06. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17189487 Free PMC article.
-
Genes expressed in Pseudomonas putida during colonization of a plant-pathogenic fungus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Jul;66(7):2764-72. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.7.2764-2772.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10877766 Free PMC article.
-
Three Rings to Rule Them All: How Versatile Flavoenzymes Orchestrate the Structural Diversification of Natural Products.Biochemistry. 2022 Jan 18;61(2):47-56. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00763. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 34962769 Free PMC article.
-
Anaerobic catabolism of aromatic compounds: a genetic and genomic view.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009 Mar;73(1):71-133. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19258534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martínez-Blanco H, Reglero A, Rodríguez-Aparicio L B, Luengo J M. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7084–7090. - PubMed
-
- Miñambres B, Martínez-Blanco H, Olivera E R, García B, Díez B, Barredo J L, Moreno M A, Schleissner C, Salto F, Luengo J M. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:33531–33538. - PubMed
-
- Olivera E R, Reglero A, Martínez-Blanco H, Fernández-Medarde A, Moreno M A, Luengo J M. Eur J Biochem. 1994;221:375–381. - PubMed
-
- Frischauf A M, Lehrach H, Poustka A, Murray N. J Mol Biol. 1983;170:827–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

