Electrostatic interactions between rotor and stator in the bacterial flagellar motor
- PMID: 9600984
- PMCID: PMC27776
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6436
Electrostatic interactions between rotor and stator in the bacterial flagellar motor
Abstract
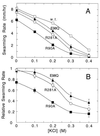
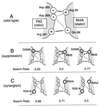
Bacterial flagellar motors rotate, obtaining power from the membrane gradient of protons or, in some species, sodium ions. Torque generation in the flagellar motor must involve interactions between components of the rotor and components of the stator. Sites of interaction between the rotor and stator have not been identified. Mutational studies of the rotor protein FliG and the stator protein MotA showed that both proteins contain charged residues essential for motor rotation. This suggests that functionally important electrostatic interactions might occur between the rotor and stator. To test this proposal, we examined double mutants with charged-residue substitutions in both the rotor protein FliG and the stator protein MotA. Several combinations of FliG mutations with MotA mutations exhibited strong synergism, whereas others showed strong suppression, in a pattern that indicates that the functionally important charged residues of FliG interact with those of MotA. These results identify a functionally important site of interaction between the rotor and stator and suggest a hypothesis for electrostatic interactions at the rotor-stator interface.
Figures
References
-
- Blair D F. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:489–522. - PubMed
-
- Macnab R M. In: Escherichia coli and Salmonella, Cell and Molecular Biology. Neidhardt F C, editor. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1995. pp. 123–145.
-
- Matsuura S, Shioi J-I, Imae Y. FEBS Lett. 1977;82:187–190. - PubMed
-
- Glagolev A N, Skulachev V P. Nature (London) 1978;272:280–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

