Cholesterol depletion inhibits the generation of beta-amyloid in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 9600988
- PMCID: PMC27798
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6460
Cholesterol depletion inhibits the generation of beta-amyloid in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
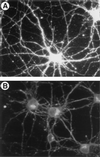
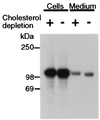
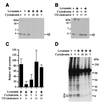
The amyloid precursor protein (APP) plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. During intracellular transport APP undergoes a series of proteolytic cleavages that lead to the release either of an amyloidogenic fragment called beta-amyloid (Abeta) or of a nonamyloidogenic secreted form consisting of the ectodomain of APP (APPsec). It is Abeta that accumulates in the brain lesions that are thought to cause the disease. By reducing the cellular cholesterol level of living hippocampal neurons by 70% with lovastatin and methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, we show that the formation of Abeta is completely inhibited while the generation of APPsec is unperturbed. This inhibition of Abeta formation is accompanied by increased solubility in the detergent Triton X-100 and is fully reversible by the readdition of cholesterol to previously depleted cells. Our results show that cholesterol is required for Abeta formation to occur and imply a link between cholesterol, Abeta, and Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

References
-
- Kang J, Lemaire H G, Unterbeck A, Salbaum J M, Masters C L, Grzeschik K H, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Muller H B. Nature (London) 1987;325:733–736. - PubMed
-
- Haass C, Selkoe D J. Cell. 1993;75:1039–1042. - PubMed
-
- Price D L, Sisodia S S, Gandy S E. Curr Opin Neurol. 1995;8:268–274. - PubMed
-
- Tanzi R E, Kovacs D M, Kim T W, Moir R D, Guenette S Y, Wasco W. Neurobiol Dis. 1996;3:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe D J. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:373–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

