alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson's disease and dementia with lewy bodies
- PMID: 9600990
- PMCID: PMC27806
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6469
alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson's disease and dementia with lewy bodies
Abstract
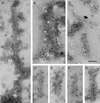
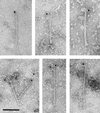
Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites are the defining neuropathological characteristics of Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. They are made of abnormal filamentous assemblies of unknown composition. We show here that Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites from Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies are stained strongly by antibodies directed against amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal sequences of alpha-synuclein, showing the presence of full-length or close to full-length alpha-synuclein. The number of alpha-synuclein-stained structures exceeded that immunoreactive for ubiquitin, which is currently the most sensitive marker of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. Staining for alpha-synuclein thus will replace staining for ubiquitin as the preferred method for detecting Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. We have isolated Lewy body filaments by a method used for the extraction of paired helical filaments from Alzheimer's disease brain. By immunoelectron microscopy, extracted filaments were labeled strongly by anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies. The morphologies of the 5- to 10-nm filaments and their staining characteristics suggest that extended alpha-synuclein molecules run parallel to the filament axis and that the filaments are polar structures. These findings indicate that alpha-synuclein forms the major filamentous component of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites.
Figures



References
-
- Lewy F H. Handbuch der Neurologie. Vol. 3. 1912. pp. 920–933.
-
- Trétiakoff M C. Ph.D. thesis. University of Paris; 1919.
-
- Forno L S. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996;55:259–272. - PubMed
-
- Duffy P E, Tennyson V M. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965;24:398–414. - PubMed
-
- Roy S, Wolman L. J Pathol. 1969;99:39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

